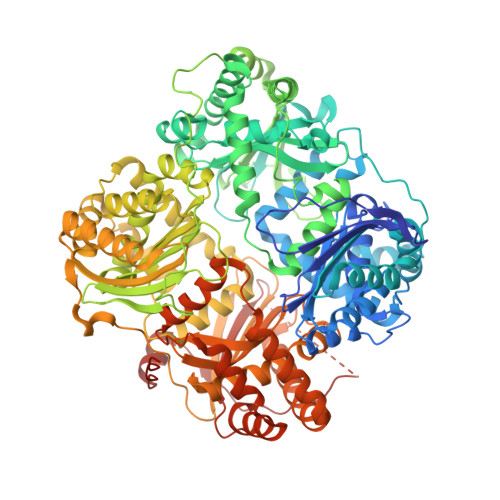
Ubiquitin is a novel substrate for human insulin-degrading enzyme.
Ralat, L.A., Kalas, V., Zheng, Z., Goldman, R.D., Sosnick, T.R., Tang, W.J.(2011) J Mol Biol 406: 454-466
- PubMed: 21185309
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmb.2010.12.026
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
3OFI - PubMed Abstract:
Insulin-degrading enzyme (IDE) can degrade insulin and amyloid-β, peptides involved in diabetes and Alzheimer's disease, respectively. IDE selects its substrates based on size, charge, and flexibility. From these criteria, we predict that IDE can cleave and inactivate ubiquitin (Ub). Here, we show that IDE cleaves Ub in a biphasic manner, first, by rapidly removing the two C-terminal glycines (k(cat)=2 s(-1)) followed by a slow cleavage between residues 72 and 73 (k(cat)=0.07 s(-1)), thereby producing the inactive 1-74 fragment of Ub (Ub1-74) and 1-72 fragment of Ub (Ub1-72). IDE is a ubiquitously expressed cytosolic protein, where monomeric Ub is also present. Thus, Ub degradation by IDE should be regulated. IDE is known to bind the cytoplasmic intermediate filament protein nestin with high affinity. We found that nestin potently inhibits the cleavage of Ub by IDE. In addition, Ub1-72 has a markedly increased affinity for IDE (∼90-fold). Thus, the association of IDE with cellular regulators and product inhibition by Ub1-72 can prevent inadvertent proteolysis of cellular Ub by IDE. Ub is a highly stable protein. However, IDE instead prefers to degrade peptides with high intrinsic flexibility. Indeed, we demonstrate that IDE is exquisitely sensitive to Ub stability. Mutations that only mildly destabilize Ub (ΔΔG<0.6 kcal/mol) render IDE hypersensitive to Ub with rate enhancements greater than 12-fold. The Ub-bound IDE structure and IDE mutants reveal that the interaction of the exosite with the N-terminus of Ub guides the unfolding of Ub, allowing its sequential cleavages. Together, our studies link the control of Ub clearance with IDE.
Organizational Affiliation:
Ben May Department for Cancer Research, The University of Chicago, 929 East 57th Street, Chicago, IL 60637, USA.