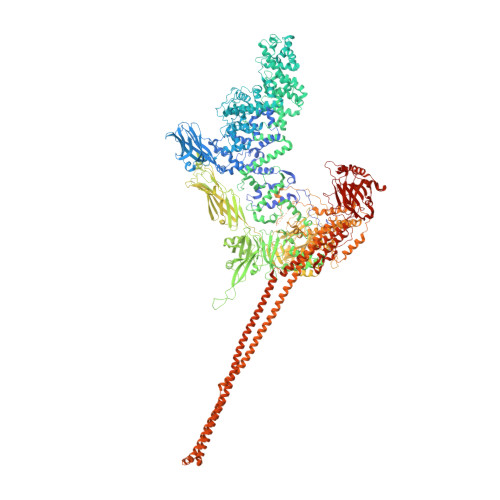
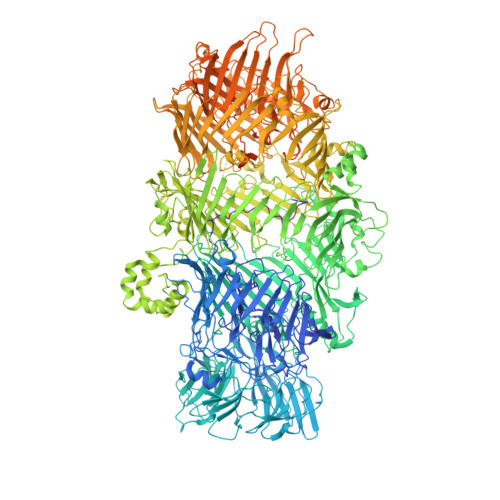
Structure of a Tc holotoxin pore provides insights into the translocation mechanism.
Roderer, D., Hofnagel, O., Benz, R., Raunser, S.(2019) Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 116: 23083-23090
- PubMed: 31666324
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1909821116
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
6SUE, 6SUF - PubMed Abstract:
Tc toxins are modular toxin systems of insect and human pathogenic bacteria. They are composed of a 1.4-MDa pentameric membrane translocator (TcA) and a 250-kDa cocoon (TcB and TcC) encapsulating the 30-kDa toxic enzyme (C terminus of TcC). Binding of Tc toxins to target cells and a pH shift trigger the conformational transition from the soluble prepore state to the membrane-embedded pore. Subsequently, the toxic enzyme is translocated and released into the cytoplasm. A high-resolution structure of a holotoxin embedded in membranes is missing, leaving open the question of whether TcB-TcC has an influence on the conformational transition of TcA. Here we show in atomic detail a fully assembled 1.7-MDa Tc holotoxin complex from Photorhabdus luminescens in the membrane. We find that the 5 TcA protomers conformationally adapt to fit around the cocoon during the prepore-to-pore transition. The architecture of the Tc toxin complex allows TcB-TcC to bind to an already membrane-embedded TcA pore to form a holotoxin. Importantly, assembly of the holotoxin at the membrane results in spontaneous translocation of the toxic enzyme, indicating that this process is not driven by a proton gradient or other energy source. Mammalian lipids with zwitterionic head groups are preferred over other lipids for the integration of Tc toxins. In a nontoxic Tc toxin variant, we can visualize part of the translocating toxic enzyme, which transiently interacts with alternating negative charges and hydrophobic stretches of the translocation channel, providing insights into the mechanism of action of Tc toxins.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Structural Biochemistry, Max Planck Institute of Molecular Physiology, 44227 Dortmund, Germany.