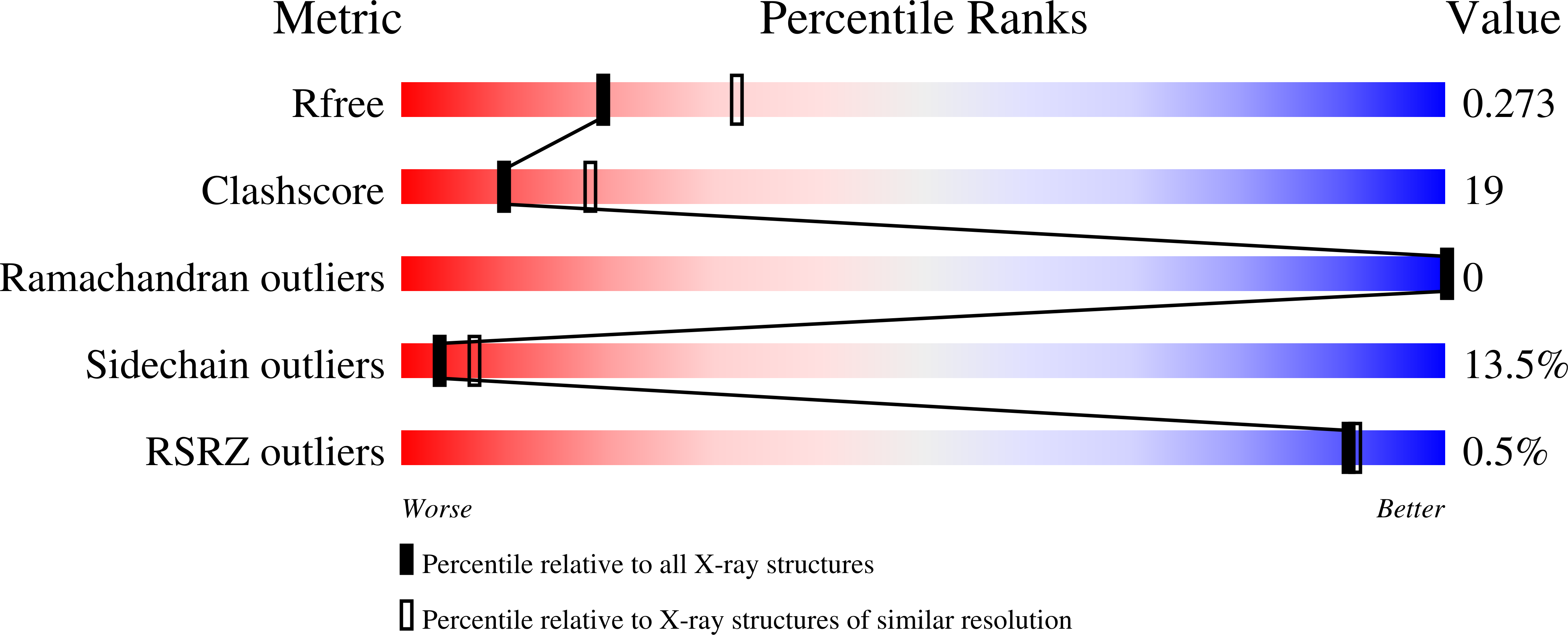
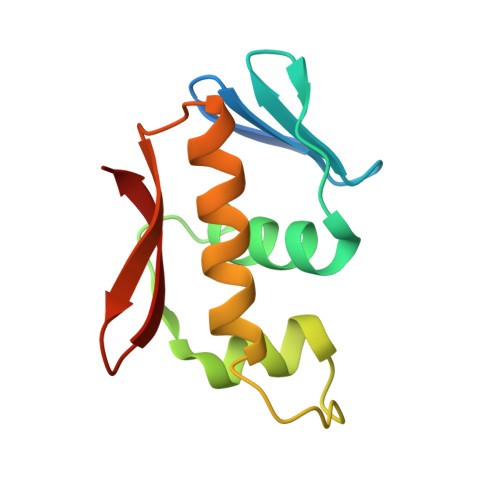
Structure of the DNA-binding domain of the response regulator SaeR from Staphylococcus aureus.
Fan, X., Zhang, X., Zhu, Y., Niu, L., Teng, M., Sun, B., Li, X.(2015) Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr 71: 1768-1776
- PubMed: 26249357
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1107/S1399004715010287
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
4QWQ - PubMed Abstract:
The SaeR/S two-component regulatory system is essential for controlling the expression of many virulence factors in Staphylococcus aureus. SaeR, a member of the OmpR/PhoB family, is a response regulator with an N-terminal regulatory domain and a C-terminal DNA-binding domain. In order to elucidate how SaeR binds to the promoter regions of target genes, the crystal structure of the DNA-binding domain of SaeR (SaeR(DBD)) was solved at 2.5 Å resolution. The structure reveals that SaeR(DBD) exists as a monomer and has the canonical winged helix-turn-helix module. EMSA experiments suggested that full-length SaeR can bind to the P1 promoter and that the binding affinity is higher than that of its C-terminal DNA-binding domain. Five key residues on the winged helix-turn-helix module were verified to be important for binding to the P1 promoter in vitro and for the physiological function of SaeR in vivo.
Organizational Affiliation:
Hefei National Laboratory for Physical Sciences at Microscale and School of Life Sciences, University of Science and Technology of China, Hefei, Anhui 230026, People's Republic of China.