Structure basis of neutralization by a novel site II/IV antibody against respiratory syncytial virus fusion protein.
Xie, Q., Wang, Z., Ni, F., Chen, X., Ma, J., Patel, N., Lu, H., Liu, Y., Tian, J.H., Flyer, D., Massare, M.J., Ellingsworth, L., Glenn, G., Smith, G., Wang, Q.(2019) PLoS One 14: e0210749-e0210749
- PubMed: 30730999
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0210749
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
6CXC - PubMed Abstract:
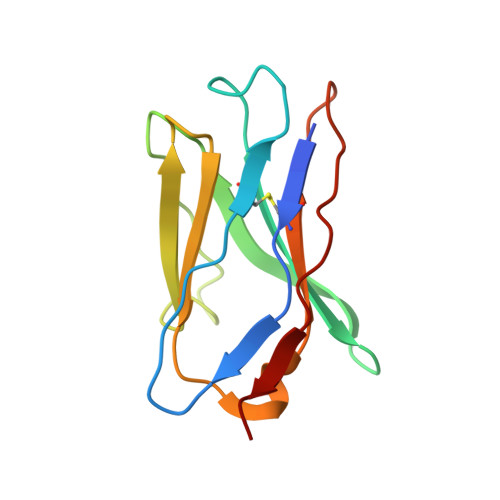
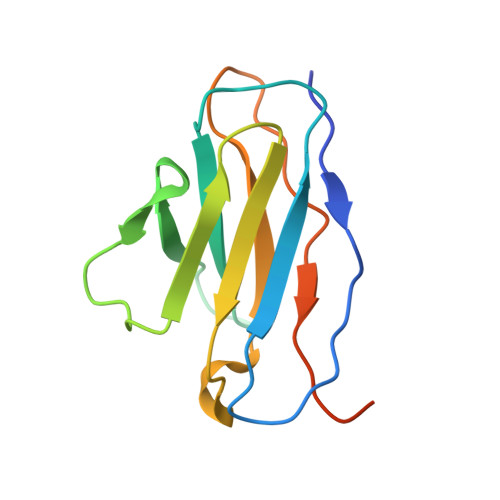
Globally, human respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) is a leading cause of lower respiratory tract infections in newborns, young children, and the elderly for which there is no vaccine. The RSV fusion (F) glycoprotein is a major target for vaccine development. Here, we describe a novel monoclonal antibody (designated as R4.C6) that recognizes both pre-fusion and post-fusion RSV F, and binds with nanomole affinity to a unique neutralizing site comprised of antigenic sites II and IV on the globular head. A 3.9 Å-resolution structure of RSV F-R4.C6 Fab complex was obtained by single particle cryo-electron microscopy and 3D reconstruction. The structure unraveled detailed interactions of R4.C6 with antigenic site II on one protomer and site IV on a neighboring protomer of post-fusion RSV F protein. These findings significantly further our understanding of the antigenic complexity of the F protein and provide new insights into RSV vaccine design.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Bioengineering, Rice University, Houston, Texas, United States of America.