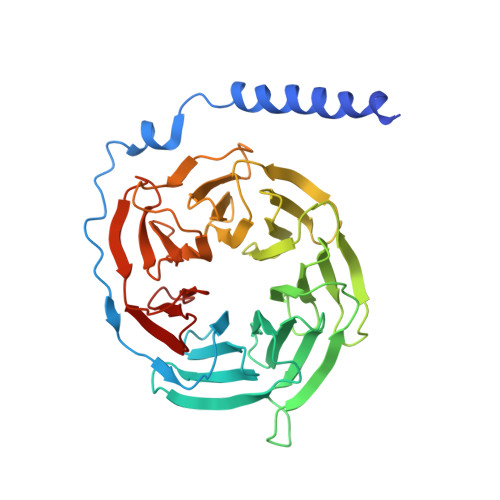
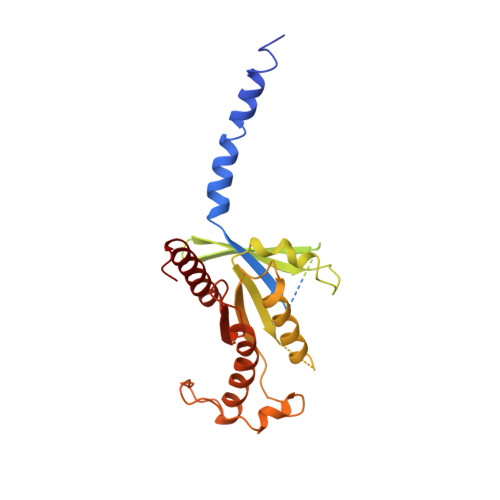
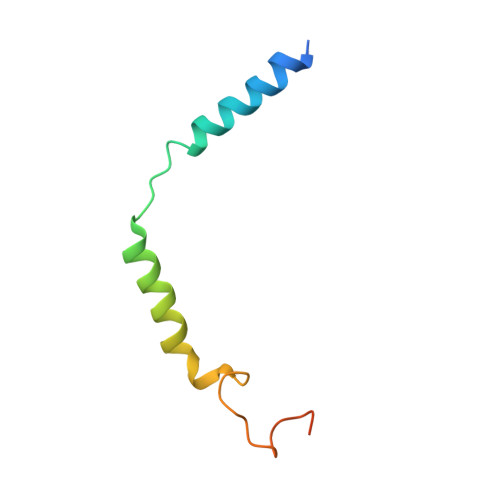
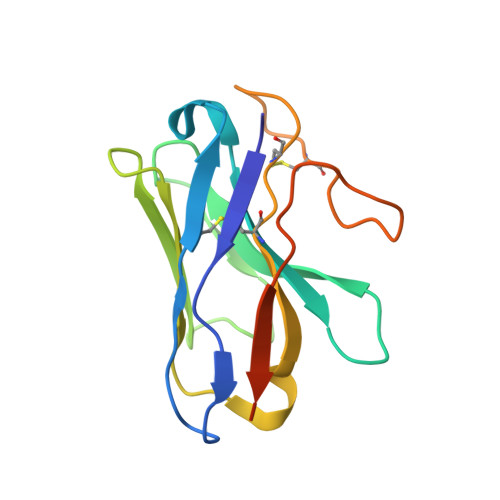
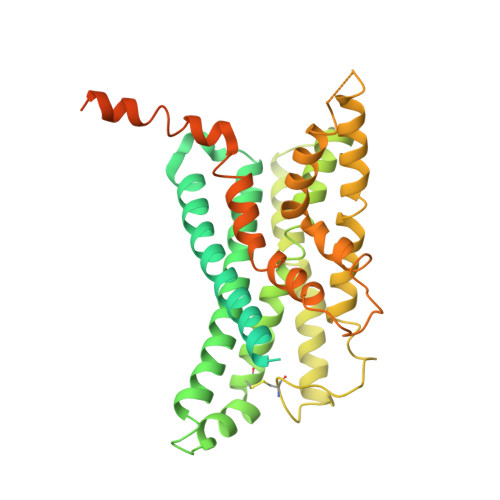
Activation of the GLP-1 receptor by a non-peptidic agonist.
Zhao, P., Liang, Y.L., Belousoff, M.J., Deganutti, G., Fletcher, M.M., Willard, F.S., Bell, M.G., Christe, M.E., Sloop, K.W., Inoue, A., Truong, T.T., Clydesdale, L., Furness, S.G.B., Christopoulos, A., Wang, M.W., Miller, L.J., Reynolds, C.A., Danev, R., Sexton, P.M., Wootten, D.(2020) Nature 577: 432-436
- PubMed: 31915381
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-019-1902-z
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
6ORV - PubMed Abstract:
Class B G-protein-coupled receptors are major targets for the treatment of chronic diseases, including diabetes and obesity 1 . Structures of active receptors reveal peptide agonists engage deep within the receptor core, leading to an outward movement of extracellular loop 3 and the tops of transmembrane helices 6 and 7, an inward movement of transmembrane helix 1, reorganization of extracellular loop 2 and outward movement of the intracellular side of transmembrane helix 6, resulting in G-protein interaction and activation 2-6 . Here we solved the structure of a non-peptide agonist, TT-OAD2, bound to the glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) receptor. Our structure identified an unpredicted non-peptide agonist-binding pocket in which reorganization of extracellular loop 3 and transmembrane helices 6 and 7 manifests independently of direct ligand interaction within the deep transmembrane domain pocket. TT-OAD2 exhibits biased agonism, and kinetics of G-protein activation and signalling that are distinct from peptide agonists. Within the structure, TT-OAD2 protrudes beyond the receptor core to interact with the lipid or detergent, providing an explanation for the distinct activation kinetics that may contribute to the clinical efficacy of this compound series. This work alters our understanding of the events that drive the activation of class B receptors.
Organizational Affiliation:
Drug Discovery Biology, Monash Institute of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Monash University, Parkville, Victoria, Australia.