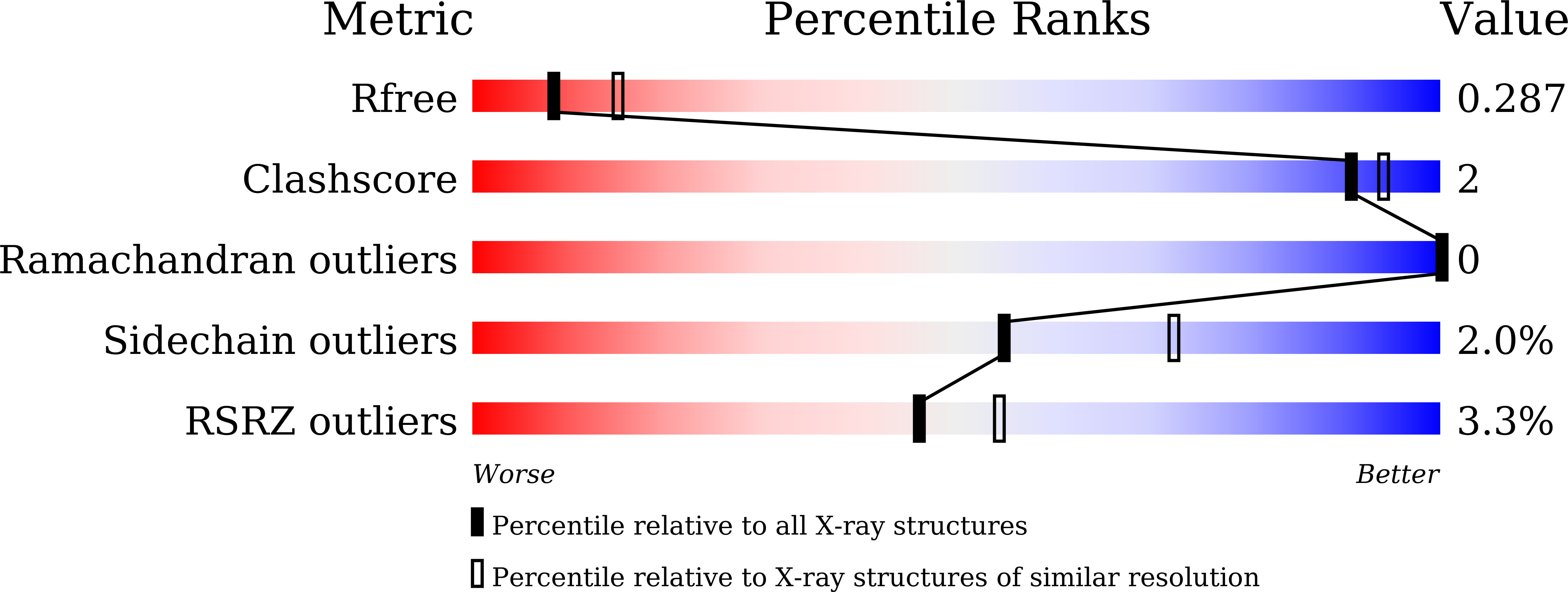
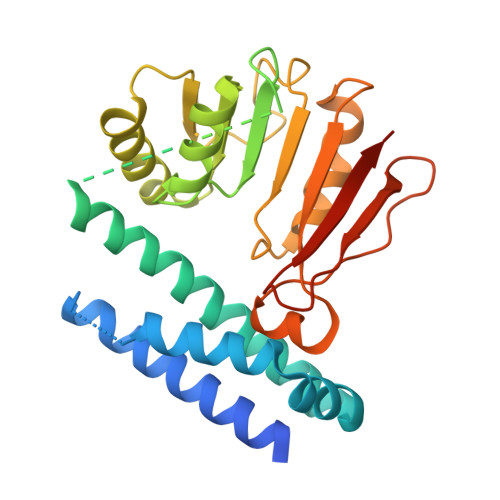
Structural insights into the ligand recognition and catalysis of the key aminobutanoyltransferase CntL in staphylopine biosynthesis.
Luo, Z., Luo, S., Ju, Y., Ding, P., Xu, J., Gu, Q., Zhou, H.(2021) FASEB J 35: e21575-e21575
- PubMed: 33826776
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1096/fj.202002287RR
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
7C7M, 7C9K, 7C9M - PubMed Abstract:
Staphylopine (StP) and other nicotianamine-like metallophores are crucial for many pathogens to acquire the transition metals from hosts during invasion. CntL from Staphylococcus aureus (SaCntL) catalyzes the condensation of the 2-aminobutyrate (Ab) moiety of S-adenosylmethionine (SAM) with D-histidine in the biosynthesis of StP. Here, we report the crystal structures of SaCntL in complex with either SAM or two products. The structure of SaCntL consists of an N-terminal four-helix bundle (holding catalytic residue E84) and a C-terminal Rossmann fold (binding the substrates). The sequence connecting the N- and C-terminal domains (N-C linker) in SaCntL was found to undergo conformational alternation between open and closed states. Our structural and biochemical analyses suggested that this intrinsically dynamic interdomain linker forms an additional structural module that plays essential roles in ligand diffusion, recognition, and catalysis. We confirmed that SaCntL stereoselectively carries out the catalysis of D-His but not its enantiomer, L-His, and we found that the N-C linker and active site of SaCntL could accommodate both enantiomers. SaCntL is likely able to bind L-His without catalysis, and as a result, L-His could show inhibitory effects toward SaCntL. These findings provide critical structural and mechanistic insights into CntL, which facilitates a better understanding of the biosynthesis of nicotianamine-like metallophores and the discovery of inhibitors of this process.
Organizational Affiliation:
Research Center for Drug Discovery and Guangdong Provincial Key Laboratory of Chiral Molecule and Drug Discovery, School of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Sun Yat-sen University, Guangzhou, China.