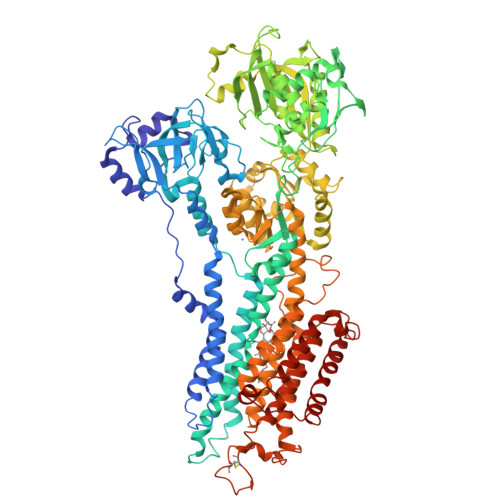
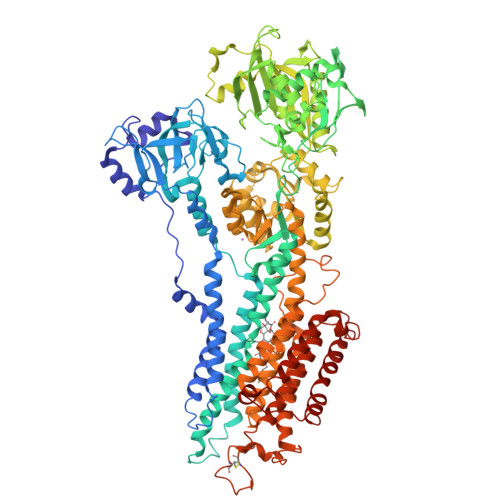
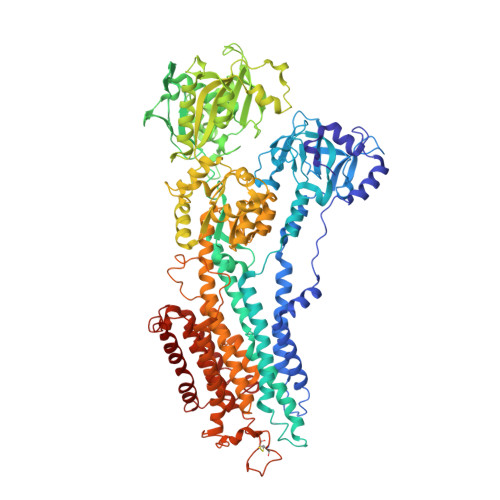
Modulatory and Catalytic Modes of ATP Binding by the Calcium Pump
Jensen, A.M., Sorensen, T.L., Olesen, C., Moller, J.V., Nissen, P.(2006) EMBO J 25: 2305
- PubMed: 16710301
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.emboj.7601135
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
2C88, 2C8K, 2C8L, 2C9M - PubMed Abstract:
We present crystal structures of the calcium-free E2 state of the sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca2+ -ATPase, stabilized by the inhibitor thapsigargin and the ATP analog AMPPCP. The structures allow us to describe the ATP binding site in a modulatory mode uncoupled from the Asp351 phosphorylation site. The Glu439 side chain interacts with AMPPCP via an Mg2+ ion in accordance with previous Fe2+ -cleavage studies implicating this residue in the ATPase cycle and in magnesium binding. Functional data on Ca2+ mediated activation indicate that the crystallized state represents an initial stage of ATP modulated deprotonation of E2, preceding the binding of Ca2+ ions in the membrane from the cytoplasmic side. We propose a mechanism of Ca2+ activation of phosphorylation leading directly from the compact E2-ATP form to the Ca2E1-ATP state. In addition, a role of Glu439 in ATP modulation of other steps of the functional cycle is suggested.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Molecular Biology, Aarhus University, Denmark.