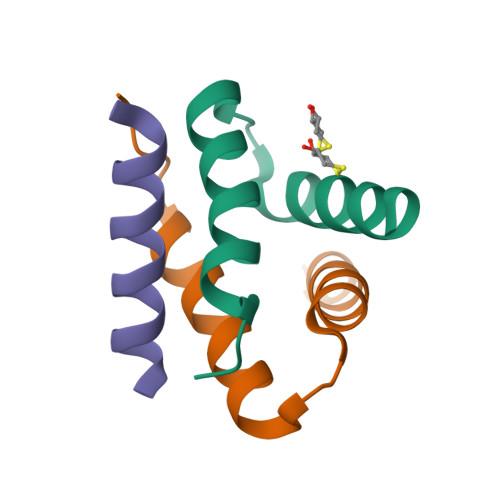
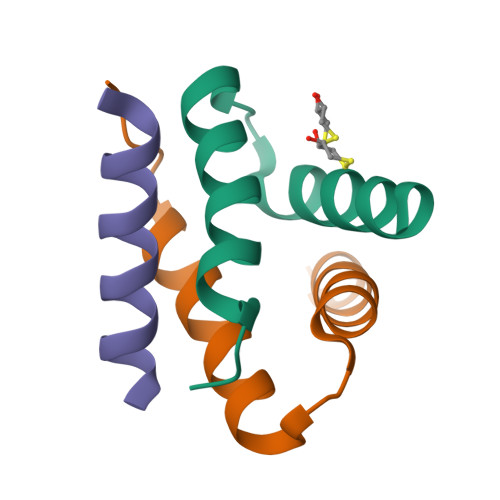
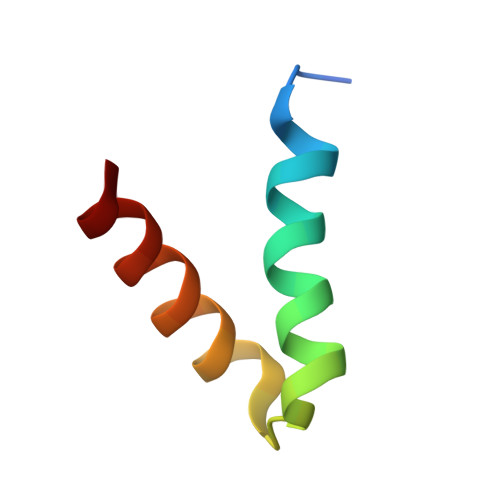
Molecular Basis of Akap Specificity for Pka Regulatory Subunits.
Gold, M.G., Lygren, B., Dokurno, P., Hoshi, N., Mcconnachie, G., Tasken, K., Carlson, C.R., Scott, J.D., Barford, D.(2006) Mol Cell 24: 383
- PubMed: 17081989
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2006.09.006
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
2IZX, 2IZY - PubMed Abstract:
Localization of cyclic AMP (cAMP)-dependent protein kinase (PKA) by A kinase-anchoring proteins (AKAPs) restricts the action of this broad specificity kinase. The high-resolution crystal structures of the docking and dimerization (D/D) domain of the RIIalpha regulatory subunit of PKA both in the apo state and in complex with the high-affinity anchoring peptide AKAP-IS explain the molecular basis for AKAP-regulatory subunit recognition. AKAP-IS folds into an amphipathic alpha helix that engages an essentially preformed shallow groove on the surface of the RII dimer D/D domains. Conserved AKAP aliphatic residues dominate interactions to RII at the predominantly hydrophobic interface, whereas polar residues are important in conferring R subunit isoform specificity. Using a peptide screening approach, we have developed SuperAKAP-IS, a peptide that is 10,000-fold more selective for the RII isoform relative to RI and can be used to assess the impact of PKA isoform-selective anchoring on cAMP-responsive events inside cells.
Organizational Affiliation:
Section of Structural Biology, Institute of Cancer Research, Chester Beatty Laboratories, 237 Fulham Road, London SW3 6JB, United Kingdom.