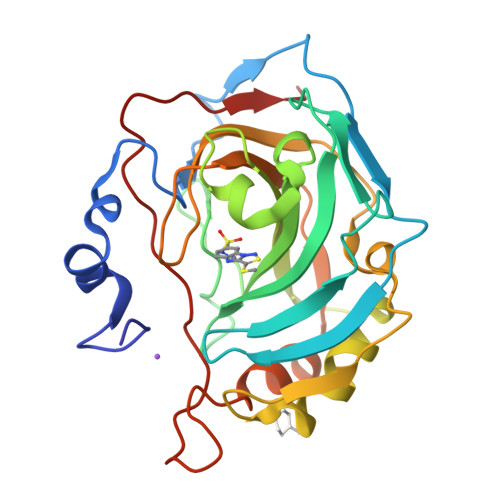
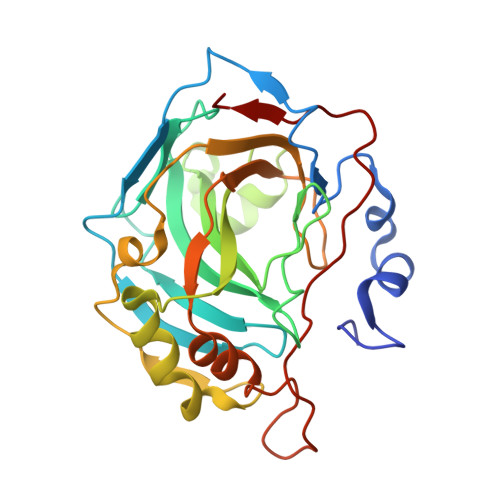
Inhibition and binding studies of carbonic anhydrase isozymes I, II and IX with benzimidazo[1,2-c][1,2,3]thiadiazole-7-sulphonamides
Baranauskiene, L., Hilvo, M., Matuliene, J., Golovenko, D., Manakova, E., Dudutiene, V., Michailoviene, V., Torresan, J., Jachno, J., Parkkila, S., Maresca, A., Supuran, C.T., Grazulis, S., Matulis, D.(2010) J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem 25: 863-870
- PubMed: 20166809
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3109/14756360903571685
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
3HLJ - PubMed Abstract:
The binding and inhibition strength of a series of benzimidazo[1,2-c][1,2,3]thiadiazole-7-sulphonamides were determined for recombinant human carbonic anhydrase isoforms I, II, and IX. The inhibition strength was determined by a stop-flow method to measure carbon dioxide hydration. Inhibitor-enzyme binding was determined by two biophysical techniques--isothermal titration calorimetry and thermal shift assay. The co-crystal structure was determined by X-ray crystallography. Comparing the results obtained using three different inhibition and binding methods increased the accuracy of compound affinity ranking and the ability to determine compound inhibitory specificity towards a particular carbonic anhydrase isoform. In most cases, all three methods yielded the same results despite using very different approaches to measure the binding and inhibition reactions. Some of the compounds studied are submicromolar inhibitors of the isoform IX, a prominent cancer target.
Organizational Affiliation:
Laboratory of Biothermodynamics and Drug Design, Institute of Biotechnology, Graičiūno 8, Vilnius, Lithuania.