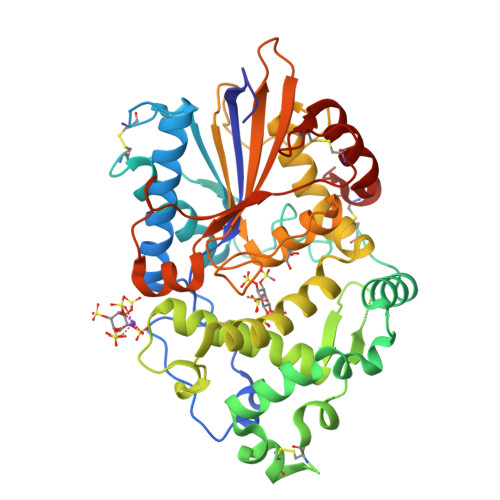
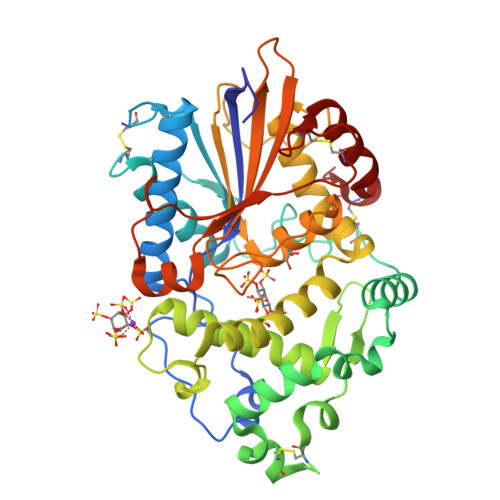
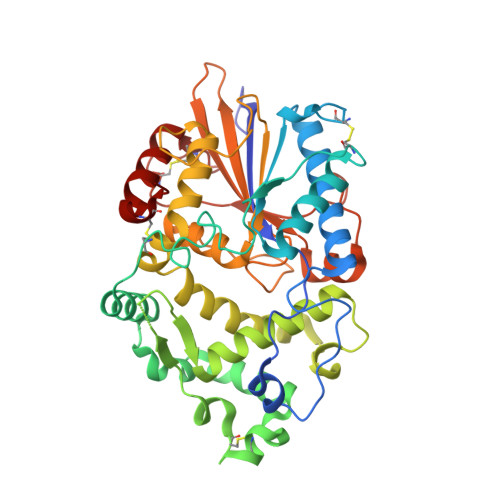
Degradation of Phytate by the 6-Phytase from Hafnia Alvei: A Combined Structural and Solution Study.
Ariza, A., Moroz, O.V., Blagova, E.V., Turkenburg, J.P., Waterman, J., Roberts, S.M., Vind, J., Sjoholm, C., Lassen, S.F., De Maria, L., Glitsoe, V., Skov, L.K., Wilson, K.S.(2013) PLoS One 8: 65062
- PubMed: 23741456
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0065062
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
4ARO, 4ARS, 4ARU, 4ARV - PubMed Abstract:
Phytases hydrolyse phytate (myo-inositol hexakisphosphate), the principal form of phosphate stored in plant seeds to produce phosphate and lower phosphorylated myo-inositols. They are used extensively in the feed industry, and have been characterised biochemically and structurally with a number of structures in the PDB. They are divided into four distinct families: histidine acid phosphatases (HAP), β-propeller phytases, cysteine phosphatases and purple acid phosphatases and also split into three enzyme classes, the 3-, 5- and 6-phytases, depending on the position of the first phosphate in the inositol ring to be removed. We report identification, cloning, purification and 3D structures of 6-phytases from two bacteria, Hafnia alvei and Yersinia kristensenii, together with their pH optima, thermal stability, and degradation profiles for phytate. An important result is the structure of the H. alvei enzyme in complex with the substrate analogue myo-inositol hexakissulphate. In contrast to the only previous structure of a ligand-bound 6-phytase, where the 3-phosphate was unexpectedly in the catalytic site, in the H. alvei complex the expected scissile 6-phosphate (sulphate in the inhibitor) is placed in the catalytic site.
Organizational Affiliation:
Structural Biology Laboratory, Department of Chemistry, University of York, York, United Kingdom.