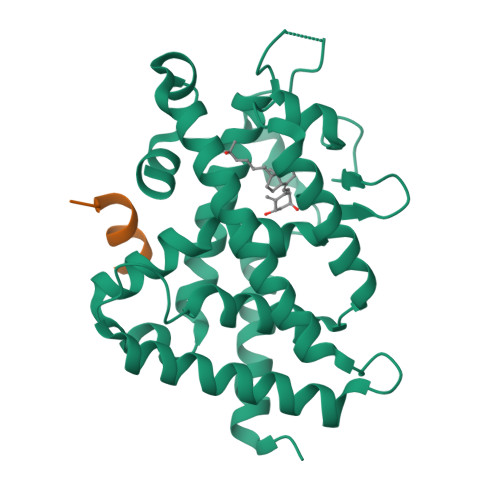
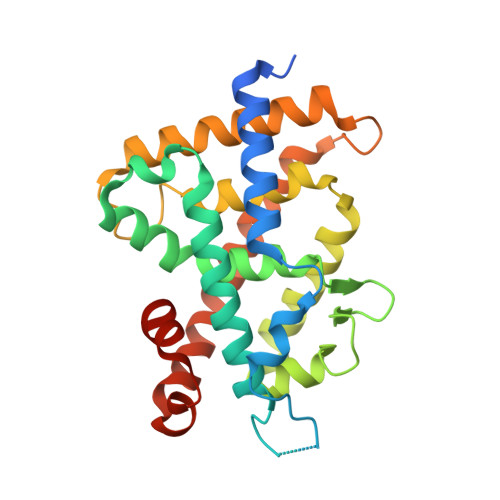
SRC2-3 binds to vitamin D receptor with high sensitivity and strong affinity
Egawa, D., Itoh, T., Kato, A., Kataoka, S., Anami, Y., Yamamoto, K.(2017) Bioorg Med Chem 25: 568-574
- PubMed: 27890450
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bmc.2016.11.020
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
5H1E - PubMed Abstract:
Vitamin D receptor (VDR) is a member of the nuclear receptor superfamily and regulates the expression of target genes through ligand binding. To express the target gene, coactivator binding to the VDR/ligand complex is essential. Although there are many coactivators in living cells, precise interactions between coactivators and VDR have not been clarified. Here, we synthesized two coactivator peptides, DRIP205-2 and SRC2-3, evaluated their affinity for the ligand-binding domain (LBD) of VDR using 1α,25-dihydroxyvitamin D 3 , partial agonist 1, and antagonist 2 by surface plasmon resonance (SPR), and assessed their interaction modes with VDR-LBD using X-ray crystallographic analysis. This study showed that the SRC2-3 peptide is more sensitive to the ligands (agonist, partial agonist, and antagonist) and shows more intimate interactions with VDR-LBD than DRIP205-2 peptide.
Organizational Affiliation:
Laboratory of Drug Design and Medicinal Chemistry, Showa Pharmaceutical University, 3-3165 Higashi-Tamagawagakuen, Machida, Tokyo 194-8543, Japan.