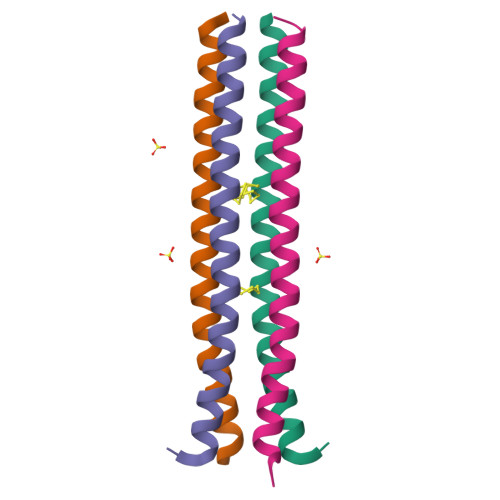Archaea S-layer nanotube from a "black smoker" in complex with cyclo-octasulfur (S8 ) rings.
McDougall, M., Francisco, O., Harder-Viddal, C., Roshko, R., Meier, M., Stetefeld, J.(2017) Proteins 85: 2209-2216
- PubMed: 28905430
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/prot.25385
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
5JR5 - PubMed Abstract:
Elemental sulfur exists primarily as an S80 ring and serves as terminal electron acceptor for a variety of sulfur-fermenting bacteria. Hyperthermophilic archaea from black smoker vents are an exciting research tool to advance our knowledge of sulfur respiration under extreme conditions. Here, we use a hybrid method approach to demonstrate that the proteinaceous cavities of the S-layer nanotube of the hyperthermophilic archaeon Staphylothermus marinus act as a storage reservoir for cyclo-octasulfur S8. Fully atomistic molecular dynamics (MD) simulations were performed and the method of multiconfigurational thermodynamic integration was employed to compute the absolute free energy for transferring a ring of elemental sulfur S8 from an aqueous bath into the largest hydrophobic cavity of a fragment of archaeal tetrabrachion. Comparisons with earlier MD studies of the free energy of hydration as a function of water occupancy in the same cavity of archaeal tetrabrachion show that the sulfur ring is energetically favored over water.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Chemistry, University of Manitoba, 144 Dysart Rd, Winnipeg, Manitoba, Canada.