Glycosylation-independent binding of monoclonal antibody toripalimab to FG loop of PD-1 for tumor immune checkpoint therapy.
Liu, H., Guo, L., Zhang, J., Zhou, Y., Zhou, J., Yao, J., Wu, H., Yao, S., Chen, B., Chai, Y., Qi, J., Gao, G.F., Tan, S., Feng, H., Yan, J.(2019) MAbs 11: 681-690
- PubMed: 30892132
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1080/19420862.2019.1596513
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
6JBT - PubMed Abstract:
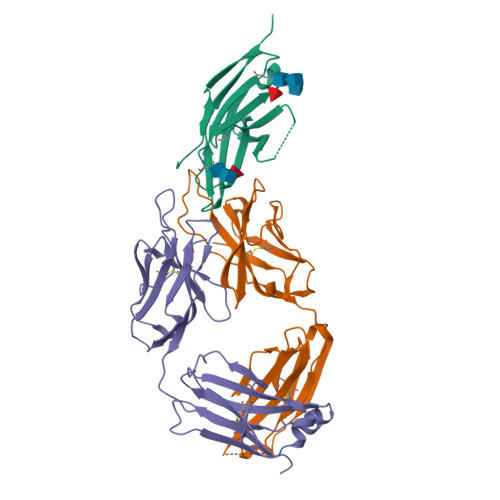
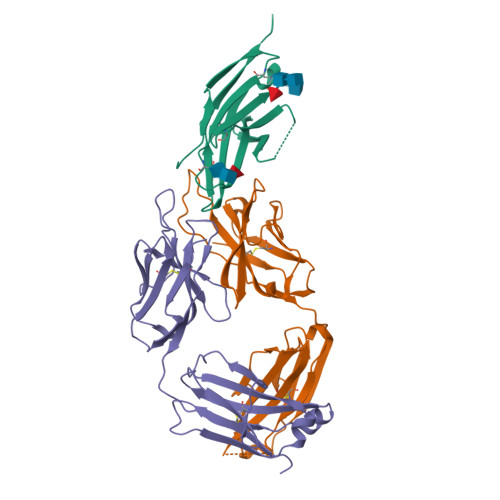
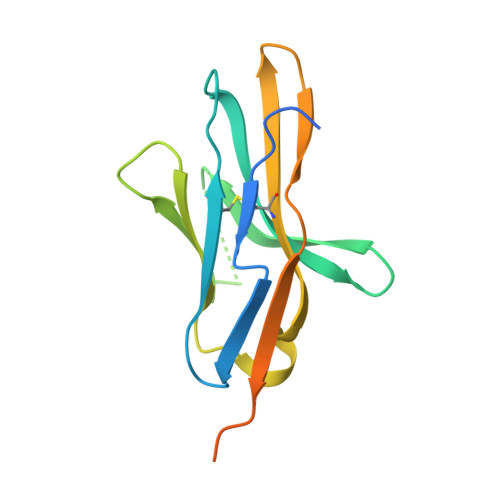
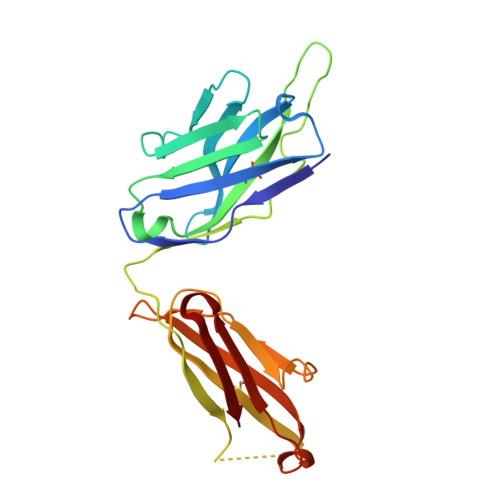
Monoclonal antibody (mAb)-based blockade of programmed cell death 1 (PD-1) or its ligand to enable antitumor T-cell immunity has been successful in treating multiple tumors. However, the structural basis of the binding mechanisms of the mAbs and PD-1 and the effects of glycosylation of PD-1 on mAb interaction are not well understood. Here, we report the complex structure of PD-1 with toripalimab, a mAb that is approved by China National Medical Products Administration as a second-line treatment for melanoma and is under multiple Phase 1-Phase 3 clinical trials in both China and the US. Our analysis reveals that toripalimab mainly binds to the FG loop of PD-1 with an unconventionally long complementarity-determining region 3 loop of the heavy chain, which is distinct from the known binding epitopes of anti-PD-1 mAbs with structural evidences. The glycan modifications of PD-1 could be observed in three potential N-linked glycosylation sites, while no substantial influences were detected to the binding of toripalimab. These findings benefit our understanding of the binding mechanisms of toripalimab to PD-1 and shed light for future development of biologics targeting PD-1. Atomic coordinates have been deposited in the Protein Data Bank under accession code 6JBT.
Organizational Affiliation:
a Department of Antibody Discovery and Engineering , Shanghai Junshi Biosciences Co., Ltd , Shanghai , China.