Structural basis of amino acid surveillance by higher-order tRNA-mRNA interactions.
Li, S., Su, Z., Lehmann, J., Stamatopoulou, V., Giarimoglou, N., Henderson, F.E., Fan, L., Pintilie, G.D., Zhang, K., Chen, M., Ludtke, S.J., Wang, Y.X., Stathopoulos, C., Chiu, W., Zhang, J.(2019) Nat Struct Mol Biol 26: 1094-1105
- PubMed: 31740854
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41594-019-0326-7
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
6PMO, 6POM - PubMed Abstract:
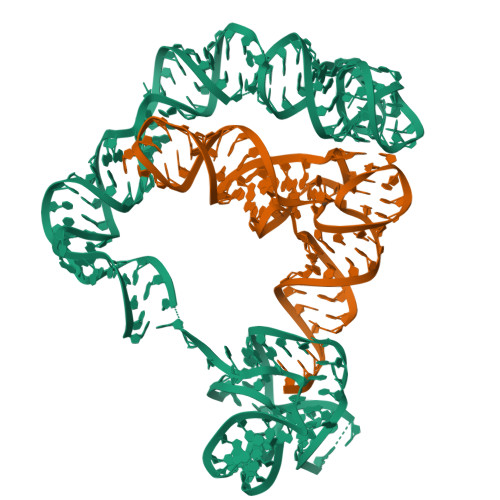
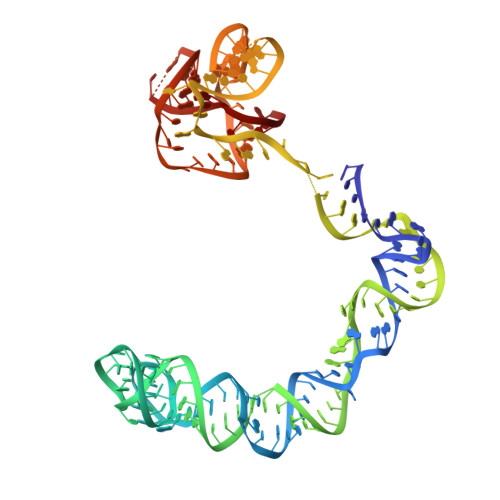
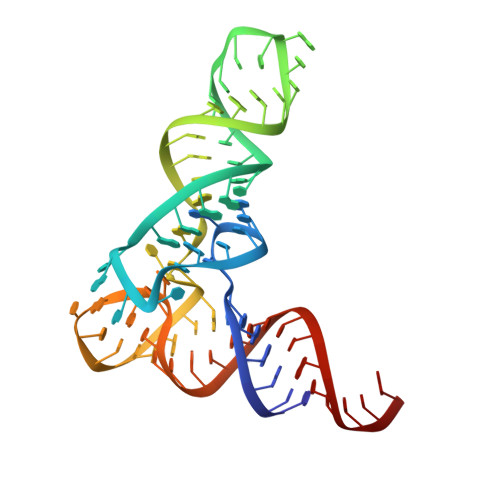
Amino acid availability in Gram-positive bacteria is monitored by T-box riboswitches. T-boxes directly bind tRNAs, assess their aminoacylation state, and regulate the transcription or translation of downstream genes to maintain nutritional homeostasis. Here, we report cocrystal and cryo-EM structures of Geobacillus kaustophilus and Bacillus subtilis T-box-tRNA complexes, detailing their multivalent, exquisitely selective interactions. The T-box forms a U-shaped molecular vise that clamps the tRNA, captures its 3' end using an elaborate 'discriminator' structure, and interrogates its aminoacylation state using a steric filter fashioned from a wobble base pair. In the absence of aminoacylation, T-boxes clutch tRNAs and form a continuously stacked central spine, permitting transcriptional readthrough or translation initiation. A modeled aminoacyl disrupts tRNA-T-box stacking, severing the central spine and blocking gene expression. Our data establish a universal mechanism of amino acid sensing on tRNAs and gene regulation by T-box riboswitches and exemplify how higher-order RNA-RNA interactions achieve multivalency and specificity.
Organizational Affiliation:
Laboratory of Molecular Biology, National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases, Bethesda, MD, USA.