Spiers Memorial Lecture: Shielding the active site: a streptavidin superoxide-dismutase chimera as a host protein for asymmetric transfer hydrogenation.
Igareta, N.V., Tachibana, R., Spiess, D.C., Peterson, R.L., Ward, T.R.(2023) Faraday Discuss
- PubMed: 36924204
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1039/d3fd00034f
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
7B74 - PubMed Abstract:
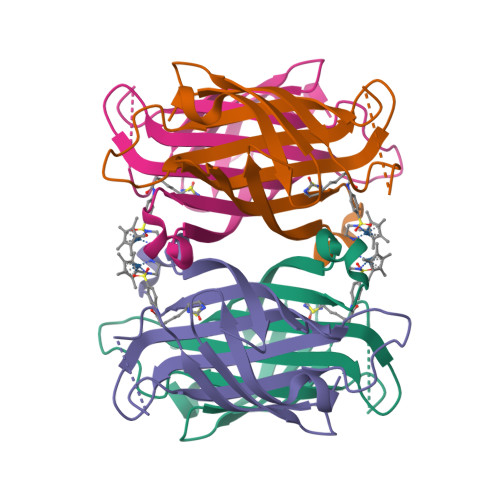
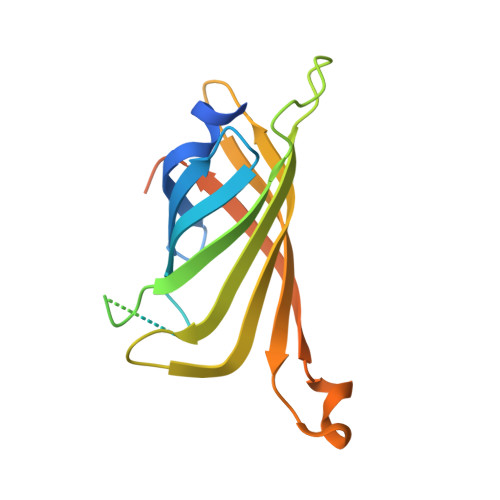
By anchoring a metal cofactor within a host protein, so-called artificial metalloenzymes can be generated. Such hybrid catalysts combine the versatility of transition metals in catalyzing new-to-nature reactions with the power of genetic-engineering to evolve proteins. With the aim of gaining better control over second coordination-sphere interactions between a streptavidin host-protein (Sav) and a biotinylated cofactor, we engineered a hydrophobic dimerization domain, borrowed from superoxide dismutase C (SOD), on Sav's biotin-binding vestibule. The influence of the SOD dimerization domain (DD) on the performance of an asymmetric transfer hydrogenase (ATHase) resulting from anchoring a biotinylated Cp*Ir-cofactor - [Cp*Ir(biot- p -L)Cl] (1-Cl) - within Sav-SOD is reported herein. We show that, depending on the nature of the residue at position Sav S112, the introduction of the SOD DD on the biotin-binding vestibule leads to an inversion of configuration of the reduction product, as well as a fivefold increase in catalytic efficiency. The findings are rationalized by QM/MM calculations, combined with X-ray crystallography.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Chemistry, University of Basel, Mattenstrasse 24a, BPR 1096, Basel, CH-4058, Switzerland. thomas.ward@unibas.ch.