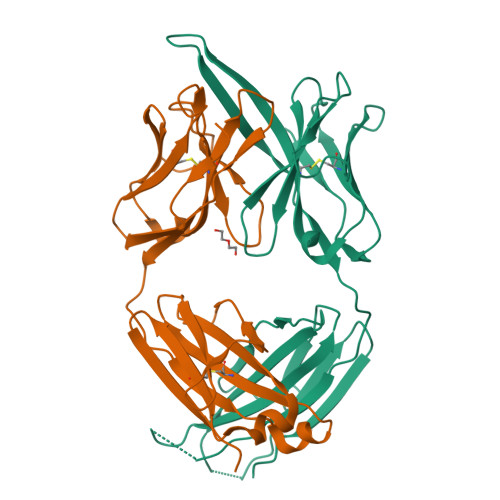
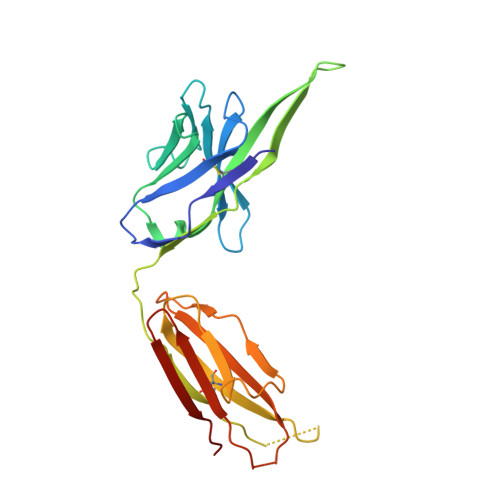
Convergence of a common solution for broad ebolavirus neutralization by glycan cap-directed human antibodies.
Murin, C.D., Gilchuk, P., Ilinykh, P.A., Huang, K., Kuzmina, N., Shen, X., Bruhn, J.F., Bryan, A.L., Davidson, E., Doranz, B.J., Williamson, L.E., Copps, J., Alkutkar, T., Flyak, A.I., Bukreyev, A., Crowe Jr., J.E., Ward, A.B.(2021) Cell Rep 35: 108984-108984
- PubMed: 33852862
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2021.108984
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
7KEJ, 7KEW, 7KEX, 7KF9, 7KFB, 7KFE, 7KFG, 7KFH - PubMed Abstract:
Antibodies that target the glycan cap epitope on the ebolavirus glycoprotein (GP) are common in the adaptive response of survivors. A subset is known to be broadly neutralizing, but the details of their epitopes and basis for neutralization are not well understood. Here, we present cryoelectron microscopy (cryo-EM) structures of diverse glycan cap antibodies that variably synergize with GP base-binding antibodies. These structures describe a conserved site of vulnerability that anchors the mucin-like domains (MLDs) to the glycan cap, which we call the MLD anchor and cradle. Antibodies that bind to the MLD cradle share common features, including use of IGHV1-69 and IGHJ6 germline genes, which exploit hydrophobic residues and form β-hairpin structures to mimic the MLD anchor, disrupt MLD attachment, destabilize GP quaternary structure, and block cleavage events required for receptor binding. Our results provide a molecular basis for ebolavirus neutralization by broadly reactive glycan cap antibodies.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Integrative Structural and Computational Biology, The Scripps Research Institute, La Jolla, CA 92037, USA.