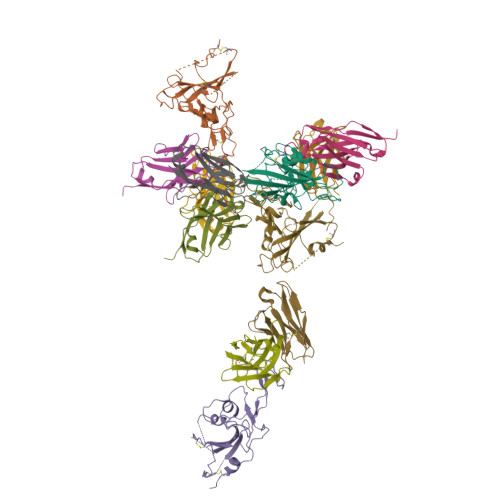
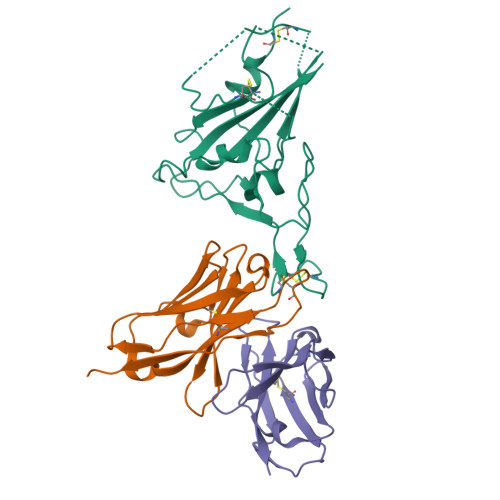
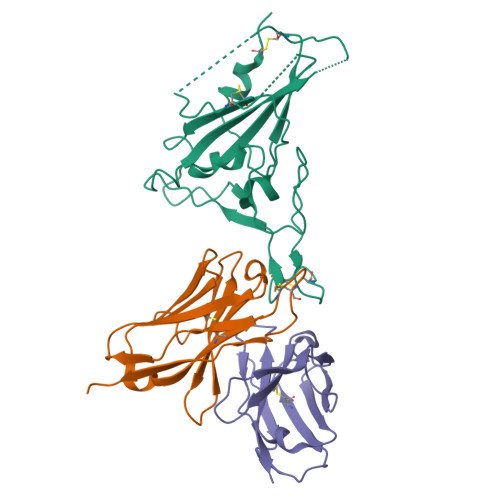
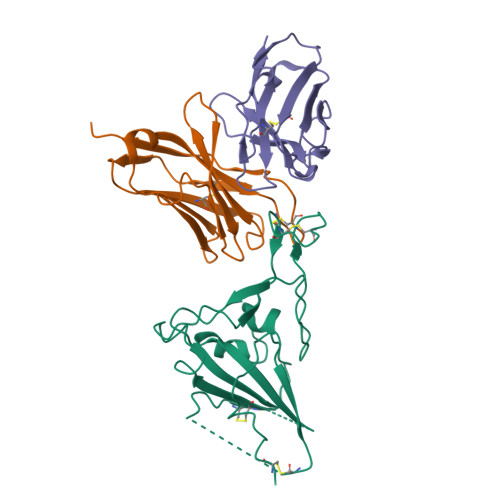
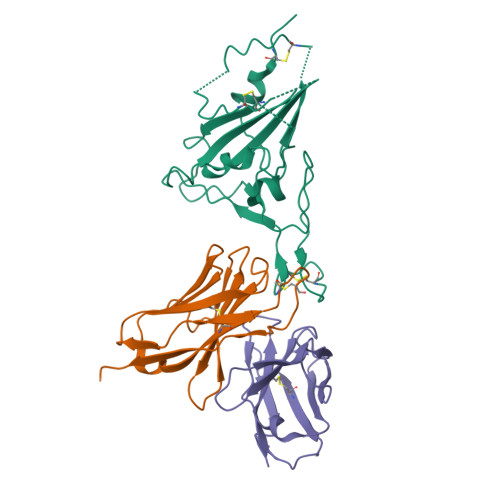
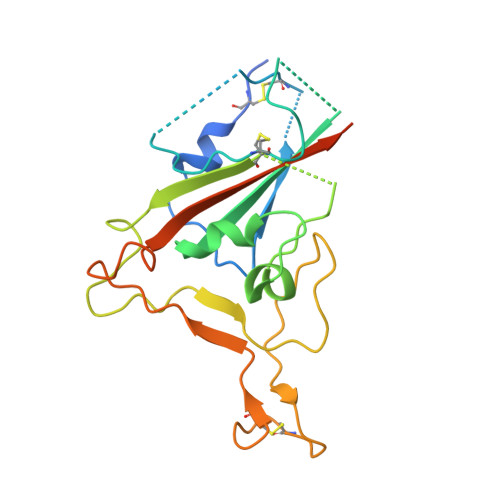
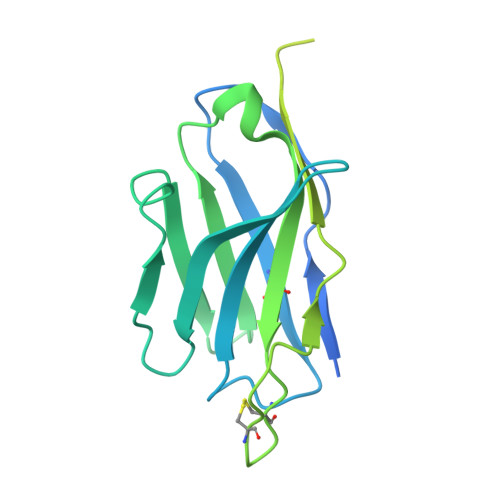
Novel super-neutralizing antibody UT28K is capable of protecting against infection from a wide variety of SARS-CoV-2 variants.
Ozawa, T., Tani, H., Anraku, Y., Kita, S., Igarashi, E., Saga, Y., Inasaki, N., Kawasuji, H., Yamada, H., Sasaki, S.I., Somekawa, M., Sasaki, J., Hayakawa, Y., Yamamoto, Y., Morinaga, Y., Kurosawa, N., Isobe, M., Fukuhara, H., Maenaka, K., Hashiguchi, T., Kishi, H., Kitajima, I., Saito, S., Niimi, H.(2022) MAbs 14: 2072455-2072455
- PubMed: 35543180
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1080/19420862.2022.2072455
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
7X7O - PubMed Abstract:
Many potent neutralizing SARS-CoV-2 antibodies have been developed and used for therapies. However, the effectiveness of many antibodies has been reduced against recently emerging SARS-CoV-2 variants, especially the Omicron variant. We identified a highly potent SARS-CoV-2 neutralizing antibody, UT28K, in COVID-19 convalescent individuals who recovered from a severe condition. UT28K showed efficacy in neutralizing SARS-CoV-2 in an in vitro assay and in vivo prophylactic treatment, and the reactivity to the Omicron strain was reduced. The structural analyses revealed that antibody UT28K Fab and SARS-CoV-2 RBD protein interactions were mainly chain-dominated antigen-antibody interactions. In addition, a mutation analysis suggested that the emergence of a UT28K neutralization-resistant SARS-CoV-2 variant was unlikely, as this variant would likely lose its competitive advantage over circulating SARS-CoV-2. Our data suggest that UT28K offers potent protection against SARS-CoV-2, including newly emerging variants.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Immunology, Faculty of Medicine, Academic Assembly, University of Toyama, Toyama, Japan.