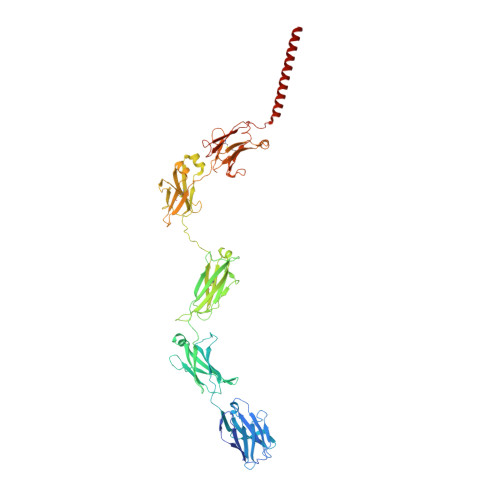
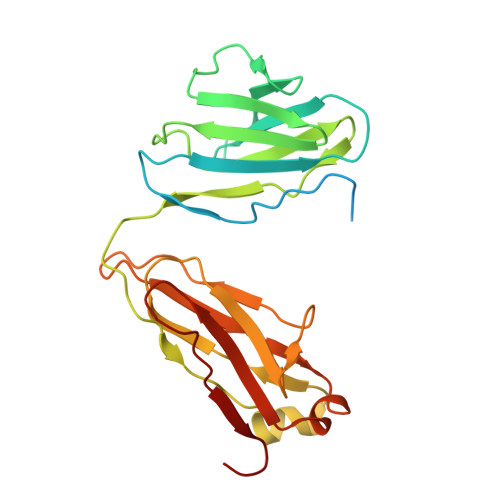
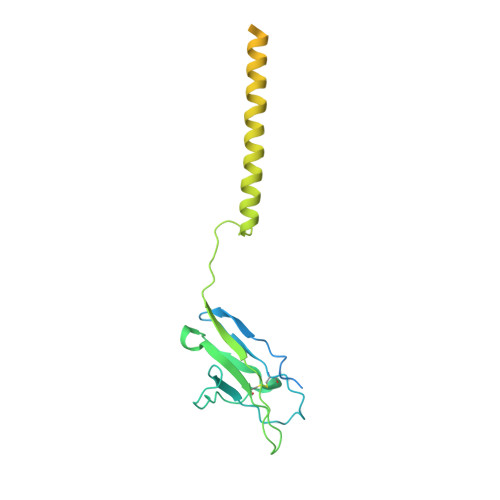
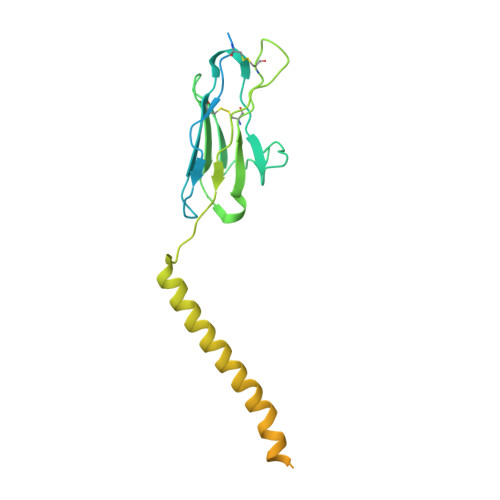
Cryo-EM structure of the human IgM B cell receptor.
Su, Q., Chen, M., Shi, Y., Zhang, X., Huang, G., Huang, B., Liu, D., Liu, Z., Shi, Y.(2022) Science 377: 875-880
- PubMed: 35981043
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1126/science.abo3923
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
7XQ8 - PubMed Abstract:
The B cell receptor (BCR) initiates immune responses through antigen recognition. We report a 3.3-angstrom cryo-electron microscopy structure of human immunoglobulin M (IgM)-BCR in the resting state. IgM-BCR comprises two heavy chains, two light chains, and the Igα/Igβ heterodimer. The ectodomains of the heavy chains closely stack against those of Igα/Igβ, with one heavy chain locked between Igα and Igβ in the juxtamembrane region. Extracellular interactions may determine isotype specificity of the BCR. The transmembrane helices of IgM-BCR form a four-helix bundle that appears to be conserved among all BCR isotypes. This structure contains 14 glycosylation sites on the IgM-BCR ectodomains and reveals three potential surface binding sites. Our work reveals the organizational principles of the BCR and may facilitate the design of antibody-based therapeutics.
Organizational Affiliation:
Research Center for Industries of the Future, Key Laboratory of Structural Biology of Zhejiang Province, School of Life Sciences, Westlake University, Institute of Biology, Westlake Institute for Advanced Study, Xihu District, Hangzhou 310024, Zhejiang Province, China.