A Retinol Derivative Inhibits SARS-CoV-2 Infection by Interrupting Spike-Mediated Cellular Entry.
Tong, L., Wang, L., Liao, S., Xiao, X., Qu, J., Wu, C., Zhu, Y., Tai, W., Huang, Y., Wang, P., Li, L., Zhang, R., Xiang, Y., Cheng, G.(2022) mBio 13: e0148522-e0148522
- PubMed: 35862773
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1128/mbio.01485-22
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
7Y42 - PubMed Abstract:
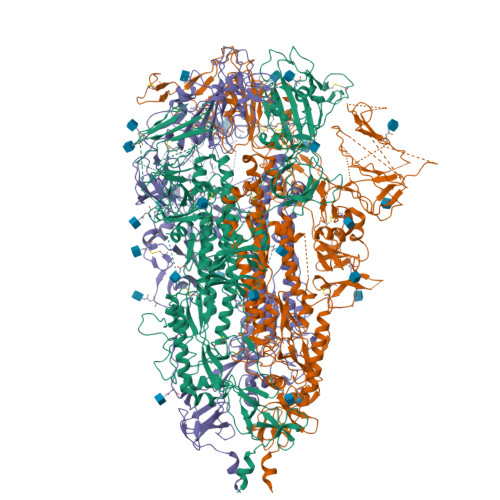
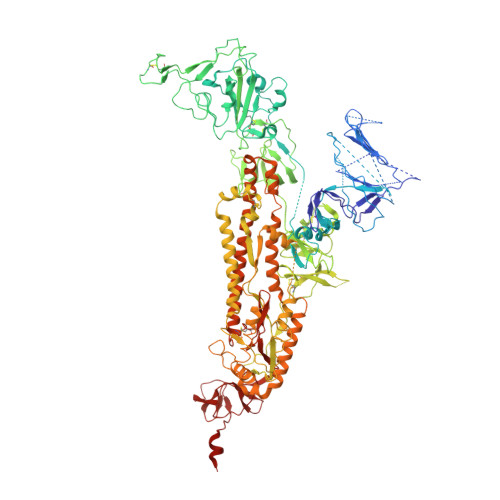
Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) is the etiological agent of the global pandemic and life-threatening coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19). Although vaccines and therapeutic antibodies are available, their efficacy is continuously undermined by rapidly emerging SARS-CoV-2 variants. Here, we found that all- trans retinoic acid (ATRA), a vitamin A (retinol) derivative, showed potent antiviral activity against all SARS-CoV-2 variants in both human cell lines and human organoids of the lower respiratory tract. Mechanistically, ATRA directly binds in a deep hydrophobic pocket of the receptor binding domain (RBD) located on the top of the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein (S) trimer. The bound ATRA mediates strong interactions between the "down" RBDs and locks most of the S trimers in an RBD "all-down" and ACE2-inaccessible inhibitory conformation. In summary, our results reveal the pharmacological biotargets and structural mechanism of ATRA and other retinoids in SARS-CoV-2 infection and suggest that ATRA and its derivatives could be potential hit compounds against a broad spectrum of coronaviruses. IMPORTANCE Retinoids, a group of compounds including vitamin A and its active metabolite all- trans retinoic acid (ATRA), regulate serial physiological activity in multiple organ systems, such as cell growth, differentiation, and apoptosis. The ATRA analogues reported to date include more than 4,000 natural and synthetic molecules that are structurally and/or functionally related to ATRA. Here, we found that ATRA showed potent antiviral activity against all SARS-CoV-2 variants by directly binding in a deep hydrophobic pocket of the receptor binding domain (RBD) located on top of the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein (S) trimer. The bound ATRA mediates strong interactions between the "down" RBDs and locks most of the S trimers in an RBD "all-down" and ACE2-inaccessible inhibitory conformation, suggesting the pharmacological feasibility of using ATRA or its derivatives as a remedy for and prevention of COVID-19 disease.
Organizational Affiliation:
Tsinghua-Peking Joint Center for Life Sciences, Beijing Frontier Research Center for Biological Structure and Beijing Advanced Innovation Center for Structural Biology, School of Medicine, Tsinghua Universitygrid.12527.33, Beijing, China.