Discovery of benzodiazepine derivatives as a new class of covalent inhibitors of SARS-CoV-2 main protease.
Wang, F., Zeng, R., Qiao, J., Xia, A., Li, Y., Li, F., Wu, Y., Liu, Y., Zhao, X., Lei, J., Yang, S.(2023) Bioorg Med Chem Lett 92: 129407-129407
- PubMed: 37437852
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bmcl.2023.129407
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
8JOP - PubMed Abstract:
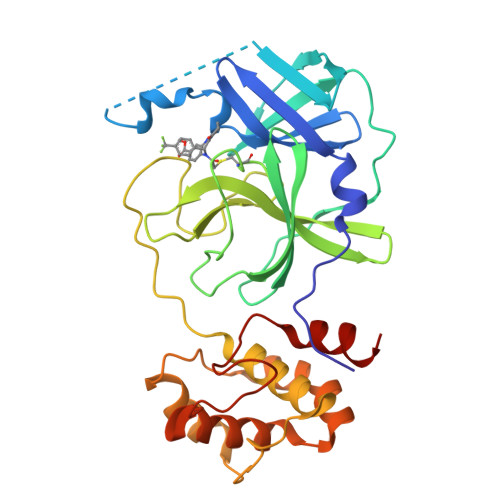
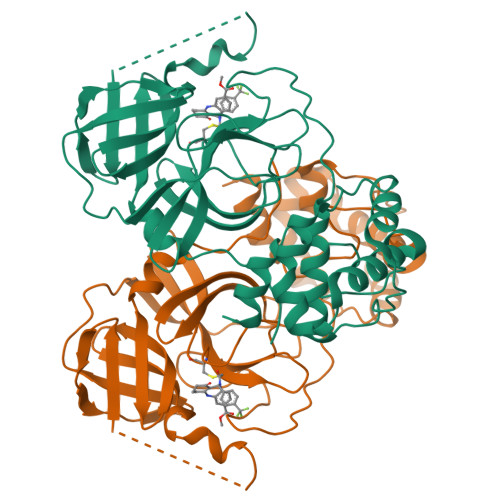
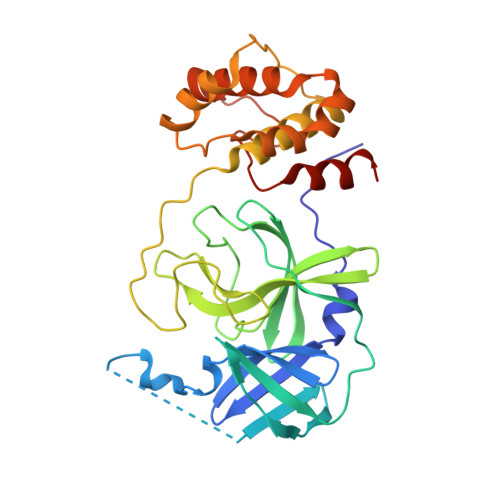
The COVID-19 pandemic has caused people immense suffering all over the world. Although the World Health Organization (WHO) has announced the end of the pandemic, the sporadic virus epidemic is still ongoing and may exist permanently. Effective antivirals against SARS-CoV-2 are important to deal with the long-term threat. The main protease (M pro ) is a crucial target for drug development due to its role in the process of virus's replication and transcription. Herein, we report benzodiazepine derivatives as a new class of M pro inhibitors. Structure-activity relationship (SAR) studies led to the discovery of the most active compound, methyl 10-(2-chloroacetyl)-1-oxo-11-(4-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl)-2,3,4,5,10,11-hexahydro-1H-dibenzo[b,e][1,4]-diazepine-7-carboxylate (11a), which shows an IC 50 value of 0.180 ± 0.004 μM. The X-ray crystal structure shows that 11a covalently binds to M pro . Collectively, we have obtained a new small molecule inhibitor targeting M pro , which can serve as a lead compound for subsequent drug discovery against SARS-CoV-2.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Biotherapy, Cancer Center and State Key Laboratory of Biotherapy, West China Hospital, Sichuan University, Chengdu 610041, China.