Structural and kinetic analysis of drug resistant mutants of HIV-1 protease.
Mahalingam, B., Louis, J.M., Reed, C.C., Adomat, J.M., Krouse, J., Wang, Y.F., Harrison, R.W., Weber, I.T.(1999) Eur J Biochem 263: 238-245
- PubMed: 10429209
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1432-1327.1999.00514.x
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1DAZ, 1DW6, 1EBK - PubMed Abstract:
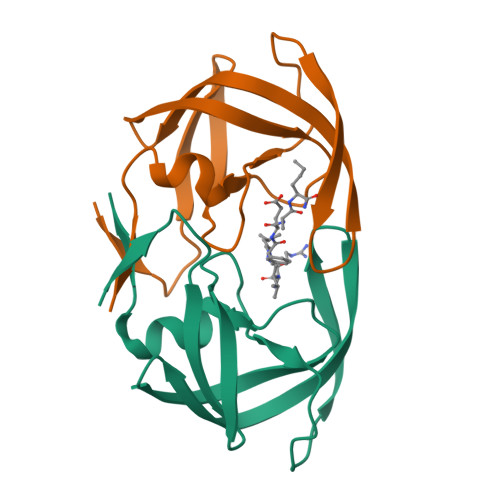
Mutants of HIV-1 protease that are commonly selected on exposure to different drugs, V82S, G48V, N88D and L90M, showed reduced catalytic activity compared to the wild-type protease on cleavage site peptides, CA-p2, p6pol-PR and PR-RT, critical for viral maturation. Mutant V82S is the least active (2-20% of wild-type protease), mutants N88D, R8Q, and L90M exhibit activities ranging from 20 to 40% and G48V from 50 to 80% of the wild-type activity. In contrast, D30N is variable in its activity on different substrates (10-110% of wild-type), with the PR-RT site being the most affected. Mutants K45I and M46L, usually selected in combination with other mutations, showed activities that are similar to (60-110%) or greater than (110-530%) wild-type, respectively. No direct relationship was observed between catalytic activity, inhibition, and structural stability. The mutants D30N and V82S were similar to wild-type protease in their stability toward urea denaturation, while R8Q, G48V, and L90M showed 1.5 to 2.7-fold decreased stability, and N88D and K45I showed 1.6 to 1.7-fold increased stability. The crystal structures of R8Q, K45I and L90M mutants complexed with a CA-p2 analog inhibitor were determined at 2.0, 1.55 and 1.88 A resolution, respectively, and compared to the wild-type structure. The intersubunit hydrophobic contacts observed in the crystal structures are in good agreement with the relative structural stability of the mutant proteases. All these results suggest that viral resistance does not arise by a single mechanism.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Microbiology and Immunology, Kimmel Cancer Center, Thomas Jefferson University, Philadelphia, USA.