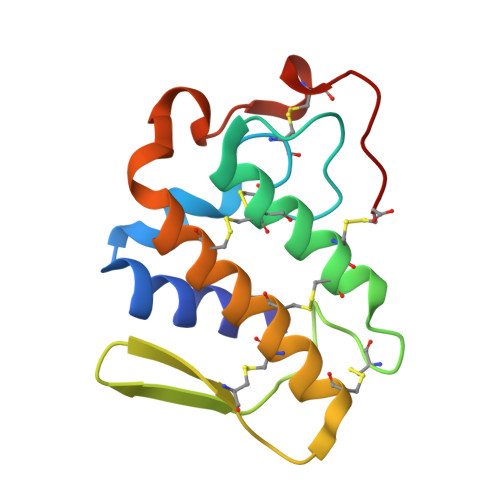
Insights into metal ion binding in phospholipases A(2): ultra high-resolution crystal structures of an acidic phospholipase A(2) in the Ca(2+) free and bound states.
Murakami, M.T., Gabdoulkhakov, A., Genov, N., Cintra, A.C., Betzel, C., Arni, R.K.(2006) Biochimie 88: 543-549
- PubMed: 16376474
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biochi.2005.10.014
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1ZL7, 1ZLB - PubMed Abstract:
The electrophile Ca(2+) is an essential multifunctional co-factor in the phospholipase A(2) mediated hydrolysis of phospholipids. Crystal structures of an acidic phospholipase A(2) from the venom of Bothrops jararacussu have been determined both in the Ca(2+) free and bound states at 0.97 and 1.60 A resolutions, respectively. In the Ca(2+) bound state, the Ca(2+) ion is penta-coordinated by a distorted pyramidal cage of oxygen and nitrogen atoms that is significantly different to that observed in structures of other Group I/II phospholipases A(2). In the absence of Ca(2+), a water molecule occupies the position of the Ca(2+) ion and the side chain of Asp49 and the calcium-binding loop adopts a different conformation.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Physics, IBILCE/UNESP, Cristovão Colombo 2265, São José do Rio Preto, SP 15054-000, Brazil.