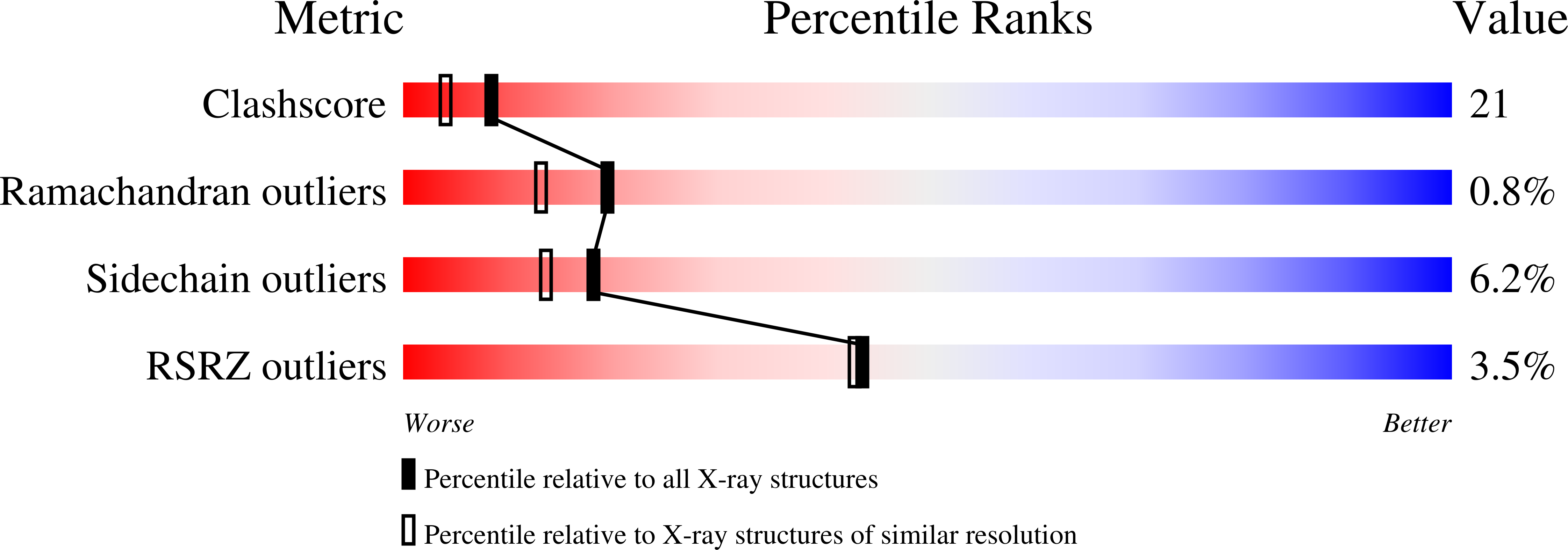
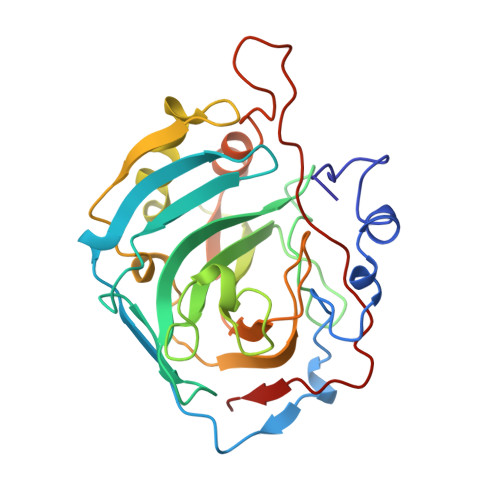
Drug-protein interactions. Refined structures of three sulfonamide drug complexes of human carbonic anhydrase I enzyme.
Chakravarty, S., Kannan, K.K.(1994) J Mol Biol 243: 298-309
- PubMed: 7932756
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1006/jmbi.1994.1655
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1AZM, 1BZM, 1CZM - PubMed Abstract:
N-unsubstituted sulfonamide drugs are widely used for opthalmic disorders. Inhibition of carbonic anhydrase enzyme is believed to be the chief reason for their therapeutic effects. Structures of three such sulfonamide drugs complexed to human carbonic anhydrase I enzyme (HCAI) refined crystallographically at 2 A resolution are reported here. The drug molecules are all bound in the active site of the enzyme, but among themselves show differences in the orientations of the sulfamido groups interacting with the essential zinc ion in the active site. The activity linked solvent molecule coordinated to zinc in the native enzyme is displaced by all the three sulfonamides. The active site loop of Leu198, Thr199 and His200 has been identified to be important for binding of the drug molecules due to their appreciable atomic displacements and intra-molecular hydrogen bonds arising out of their interactions with the sulfonamides. These interactions along with active site charge requirements are proposed to be responsible for the orientational differences of the sulfamido groups and also for differences in the inhibitory powers of the drugs. A hydrogen bond network involving solvent molecules and active site residues His200 and His67 amongst others in the native enzyme, is disrupted upon binding of methazolamide but not in the other two sulfonamides. This is the first crystallographic evidence of the possible involvement of His200 in the inhibition of HCAI. An important role of Thr199 in distinguishing between the substrate and inhibitor binding modes of HCO3- to the enzyme at high pH is also inferred.
Organizational Affiliation:
Solid State Physics Division, Bhabha Atomic Research Centre, Bombay, India.