Biochemical characterization and crystal structure determination of human heart short chain L-3-hydroxyacyl-CoA dehydrogenase provide insights into catalytic mechanism.
Barycki, J.J., O'Brien, L.K., Bratt, J.M., Zhang, R., Sanishvili, R., Strauss, A.W., Banaszak, L.J.(1999) Biochemistry 38: 5786-5798
- PubMed: 10231530
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/bi9829027
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
2HDH, 3HAD - PubMed Abstract:
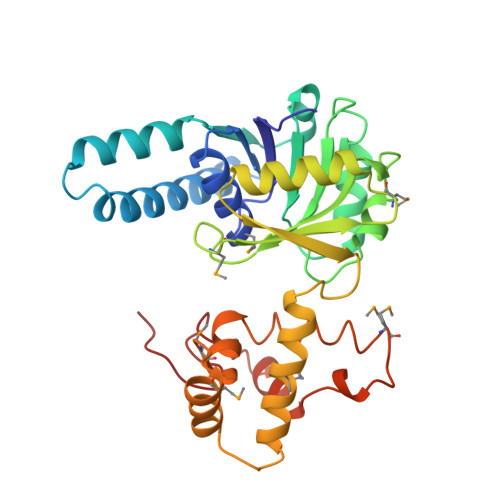
Human heart short chain L-3-hydroxyacyl-CoA dehydrogenase (SCHAD) catalyzes the oxidation of the hydroxyl group of L-3-hydroxyacyl-CoA to a keto group, concomitant with the reduction of NAD+ to NADH, as part of the beta-oxidation pathway. The homodimeric enzyme has been overexpressed in Escherichia coli, purified to homogeneity, and studied using biochemical and crystallographic techniques. The dissociation constants of NAD+ and NADH have been determined over a broad pH range and indicate that SCHAD binds reduced cofactor preferentially. Examination of apparent catalytic constants reveals that SCHAD displays optimal enzymatic activity near neutral pH, with catalytic efficiency diminishing rapidly toward pH extremes. The crystal structure of SCHAD complexed with NAD+ has been solved using multiwavelength anomalous diffraction techniques and a selenomethionine-substituted analogue of the enzyme. The subunit structure is comprised of two domains. The first domain is similar to other alpha/beta dinucleotide folds but includes an unusual helix-turn-helix motif which extends from the central beta-sheet. The second, or C-terminal, domain is primarily alpha-helical and mediates subunit dimerization and, presumably, L-3-hydroxyacyl-CoA binding. Molecular modeling studies in which L-3-hydroxybutyryl-CoA was docked into the enzyme-NAD+ complex suggest that His 158 serves as a general base, abstracting a proton from the 3-OH group of the substrate. Furthermore, the ability of His 158 to perform such a function may be enhanced by an electrostatic interaction with Glu 170, consistent with previous biochemical observations. These studies provide further understanding of the molecular basis of several inherited metabolic disease states correlated with L-3-hydroxyacyl-CoA dehydrogenase deficiencies.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Biochemistry, Molecular Biology, and Biophysics, University of Minnesota, Minneapolis 55455, USA.