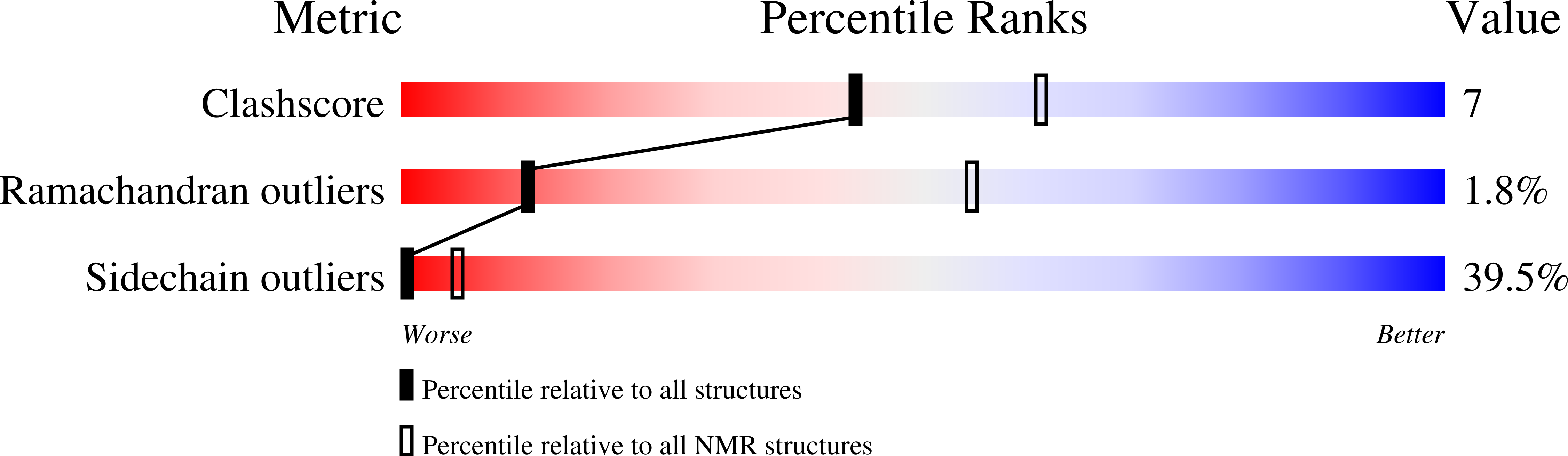Structural Insights into Rcs Phosphotransfer: The Newly Identified RcsD-ABL Domain Enhances Interaction with the Response Regulator RcsB.
Schmoe, K., Rogov, V.V., Rogova, N.Y., Lohr, F., Guntert, P., Bernhard, F., Dotsch, V.(2011) Structure 19: 577-587
- PubMed: 21481780
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.str.2011.01.012
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
2KX7 - PubMed Abstract:
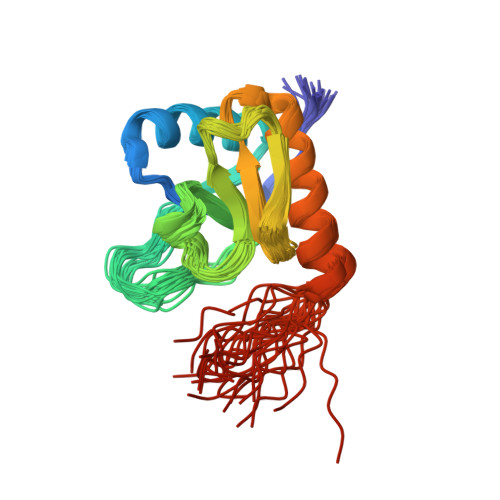
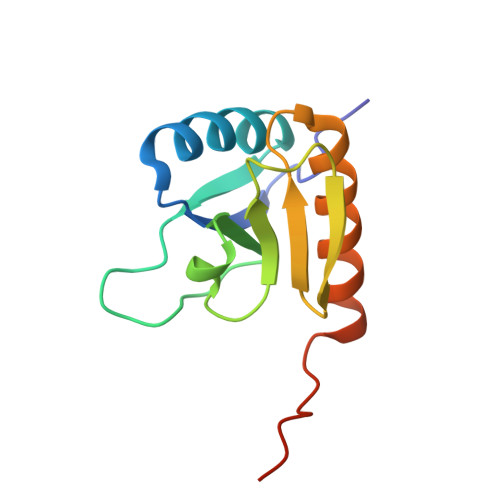
The Rcs-signaling system is one of the most remarkable phosphorelay pathways in Enterobacteriaceae, comprising several membrane-bound and soluble proteins. Within the complex phosphotransfer pathway, the histidine phosphotransferase (HPt) domain of the RcsD membrane-bound component serves as a crucial factor in modulating the phosphorylation state of the transcription factor RcsB. We have identified a new domain, RcsD-ABL, located N terminally to RcsD-HPt that interacts with RcsB as well. We have determined its structure, characterized its interaction interface with RcsB, and built a structural model of the complex of the RcsD-ABL domain with RcsB. Our results indicate that the effector domain of RcsB, which normally binds to DNA, is recognized by RcsD-ABL, whereas the HPt domain interacts with the phosphoreceiver domain of RcsB.
Organizational Affiliation:
Institute of Biophysical Chemistry and Center for Biomolecular Magnetic Resonance, Goethe University, Max-von-Laue-Strasse 9, 60438 Frankfurt/Main, Germany.