Structures of two coronavirus main proteases: implications for substrate binding and antiviral drug design.
Xue, X., Yu, H., Yang, H., Xue, F., Wu, Z., Shen, W., Li, J., Zhou, Z., Ding, Y., Zhao, Q., Zhang, X.C., Liao, M., Bartlam, M., Rao, Z.(2008) J Virol 82: 2515-2527
- PubMed: 18094151
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1128/JVI.02114-07
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
2Q6D, 2Q6F, 2Q6G - PubMed Abstract:
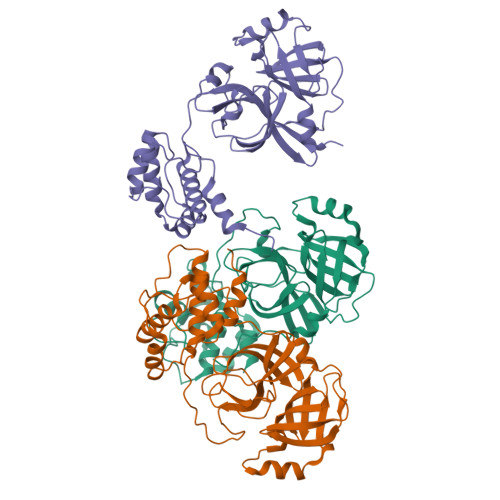
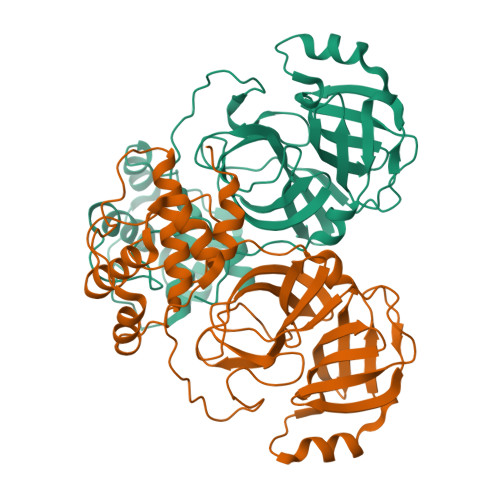
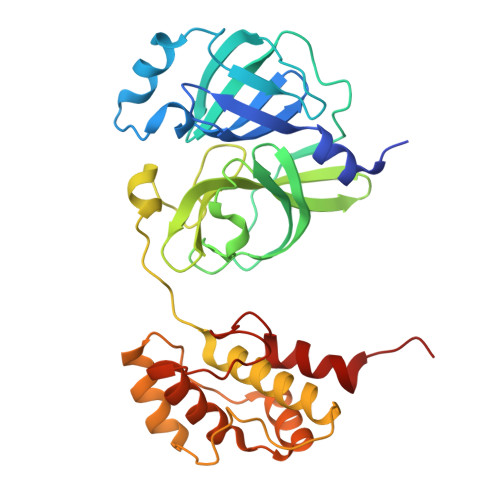
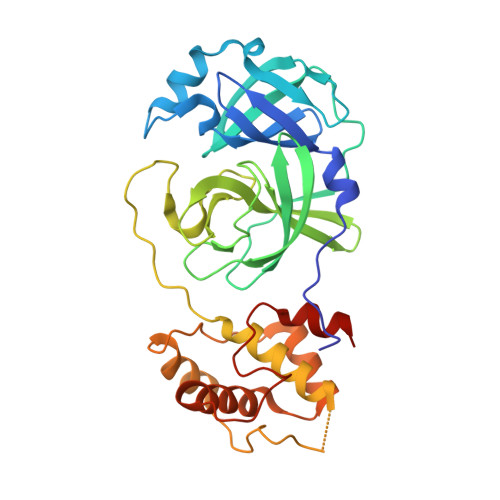
Coronaviruses (CoVs) can infect humans and multiple species of animals, causing a wide spectrum of diseases. The coronavirus main protease (M(pro)), which plays a pivotal role in viral gene expression and replication through the proteolytic processing of replicase polyproteins, is an attractive target for anti-CoV drug design. In this study, the crystal structures of infectious bronchitis virus (IBV) M(pro) and a severe acute respiratory syndrome CoV (SARS-CoV) M(pro) mutant (H41A), in complex with an N-terminal autocleavage substrate, were individually determined to elucidate the structural flexibility and substrate binding of M(pro). A monomeric form of IBV M(pro) was identified for the first time in CoV M(pro) structures. A comparison of these two structures to other available M(pro) structures provides new insights for the design of substrate-based inhibitors targeting CoV M(pro)s. Furthermore, a Michael acceptor inhibitor (named N3) was cocrystallized with IBV M(pro) and was found to demonstrate in vitro inactivation of IBV M(pro) and potent antiviral activity against IBV in chicken embryos. This provides a feasible animal model for designing wide-spectrum inhibitors against CoV-associated diseases. The structure-based optimization of N3 has yielded two more efficacious lead compounds, N27 and H16, with potent inhibition against SARS-CoV M(pro).
Organizational Affiliation:
Laboratory of Structural Biology, Life Sciences Building, Tsinghua University, Beijing 100084, China.