Corticosteroid-Binding Globulin: Structural Basis for Steroid Transport and Proteinase-Triggered Release
Klieber, M.A., Underhill, C., Hammond, G.L., Muller, Y.A.(2007) J Biological Chem 282: 29594
- PubMed: 17644521
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M705014200
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
2V95 - PubMed Abstract:
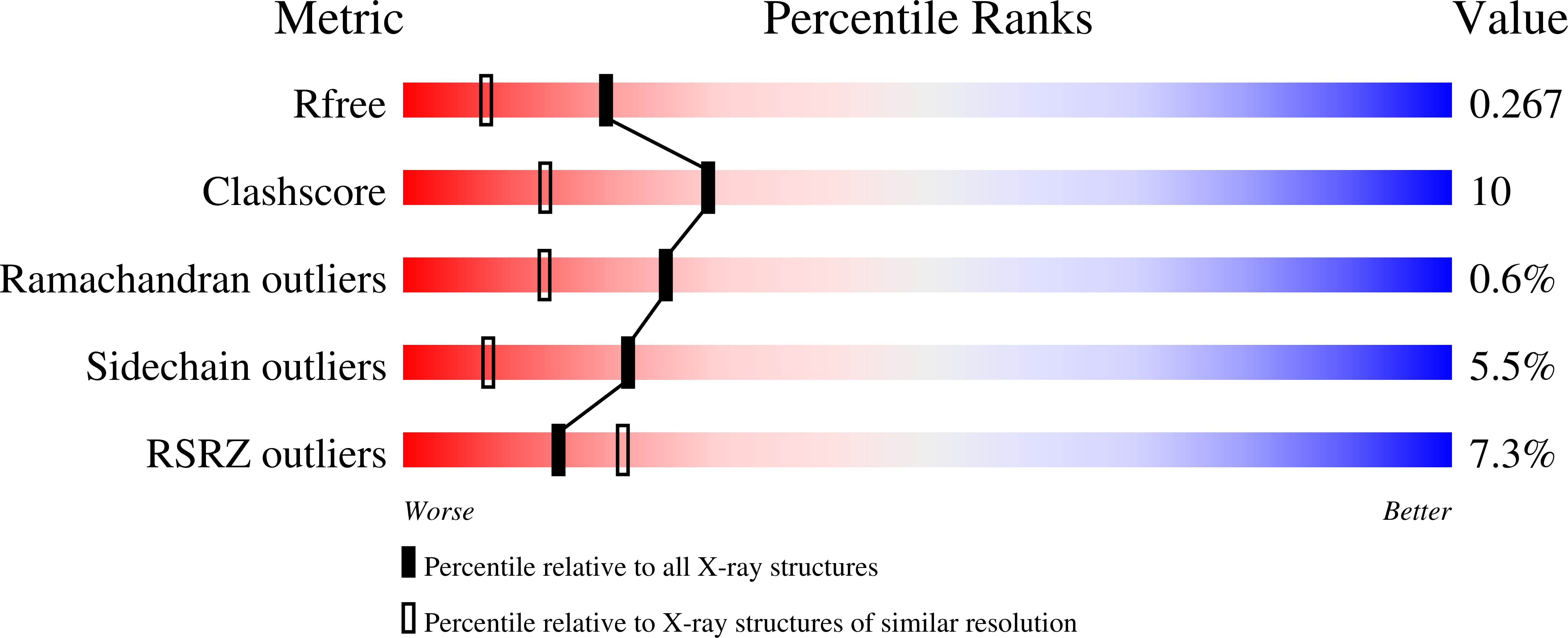
Corticosteroid-binding globulin (CBG) is a serine proteinase inhibitor (serpin) family member that transports glucocorticoids in blood and regulates their access to target cells. The 1.9A crystal structure of rat CBG shows that its steroid-binding site resembles the thyroxin-binding site in the related serpin, thyroxin-binding globulin, and mutagenesis studies have confirmed the contributions of key residues that constitute the steroid-binding pocket. Unlike thyroxin-bound thyroxin-binding globulin, the cortisol-bound CBG displays an "active" serpin conformation with the proteinase-sensitive, reactive center loop (RCL) fully expelled from the regulatory beta-sheet A. Moreover, the CBG structure allows us to predict that complete insertion of the proteolytically cleaved RCL into the serpin fold occurs in concert with a displacement and unwinding of helix D that would disrupt the steroid-binding site. This allosteric coupling between RCL positioning and occupancy of the CBG steroid-binding site, which resembles the ligand (glycosamino-glycan)-dependent activation of the thrombin inhibitory serpins heparin cofactor II and anti-thrombin RCLs, ensures both optimal recognition of CBG by target proteinases and efficient release of steroid to sites of action.
Organizational Affiliation:
Lehrstuhl für Biotechnik, Department of Biology, Friedrich-Alexander-University Erlangen-Nuremberg, D-91052 Erlangen, Germany.