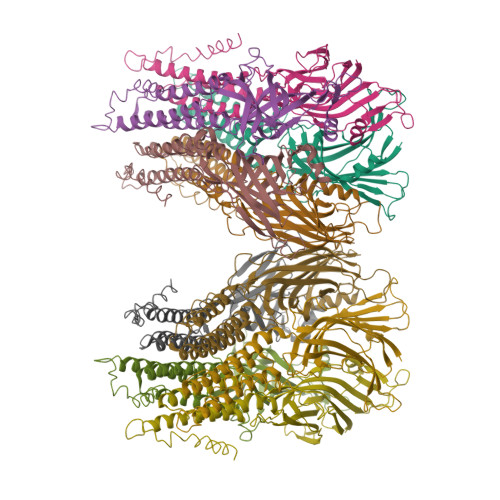
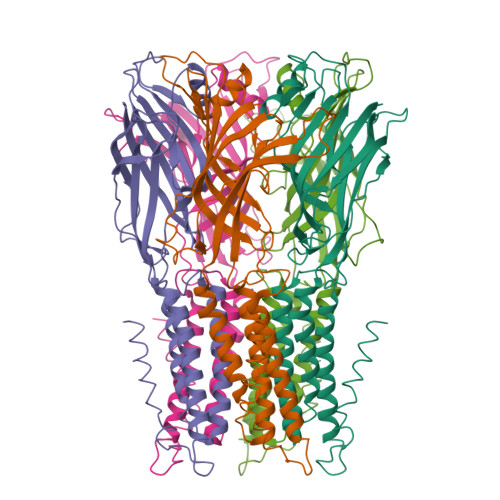
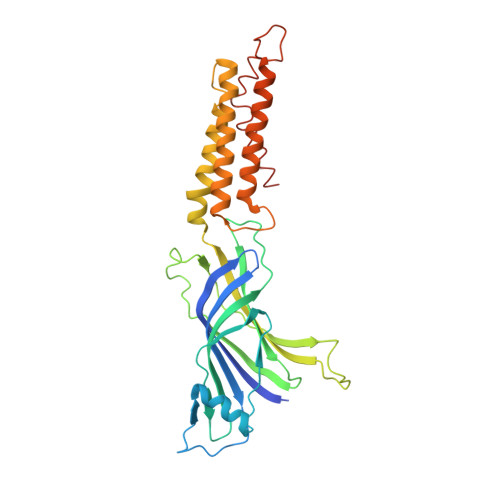
X-Ray Structure of a Prokaryotic Pentameric Ligand-Gated Ion Channel
Hilf, R.J.C., Dutzler, R.(2008) Nature 452: 375
- PubMed: 18322461
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nature06717
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
2VL0 - PubMed Abstract:
Pentameric ligand-gated ion channels (pLGICs) are key players in the early events of electrical signal transduction at chemical synapses. The family codes for a structurally conserved scaffold of channel proteins that open in response to the binding of neurotransmitter molecules. All proteins share a pentameric organization of identical or related subunits that consist of an extracellular ligand-binding domain followed by a transmembrane channel domain. The nicotinic acetylcholine receptor (nAChR) is the most thoroughly studied member of the pLGIC family (for recent reviews see refs 1-3). Two sources of structural information provided an architectural framework for the family. The structure of the soluble acetylcholine-binding protein (AChBP) defined the organization of the extracellular domain and revealed the chemical basis of ligand interaction. Electron microscopy studies of the nAChR from Torpedo electric ray have yielded a picture of the full-length protein and have recently led to the interpretation of an electron density map at 4.0 A resolution. Despite the wealth of experimental information, high-resolution structures of any family member have so far not been available. Until recently, the pLGICs were believed to be only expressed in multicellular eukaryotic organisms. The abundance of prokaryotic genome sequences, however, allowed the identification of several homologous proteins in bacterial sources. Here we present the X-ray structure of a prokaryotic pLGIC from the bacterium Erwinia chrysanthemi (ELIC) at 3.3 A resolution. Our study reveals the first structure of a pLGIC at high resolution and provides an important model system for the investigation of the general mechanisms of ion permeation and gating within the family.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Biochemistry, University of Zürich, Winterthurer Strasse 190, CH-8057 Zürich, Switzerland.