A Second Fmn-Binding Site in Yeast Nadph-Cytochrome P450 Reductase Suggests a Mechanism of Electron Transfer by Diflavin Reductases.
Lamb, D.C., Kim, Y., Yermalitskaya, L.V., Yermalitsky, V.N., Lepesheva, G.I., Kelly, S.L., Waterman, M.R., Podust, L.M.(2006) Structure 14: 51
- PubMed: 16407065
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.str.2005.09.015
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
2BF4, 2BN4 - PubMed Abstract:
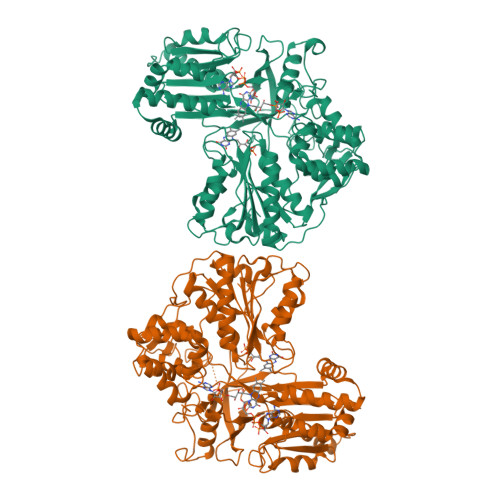
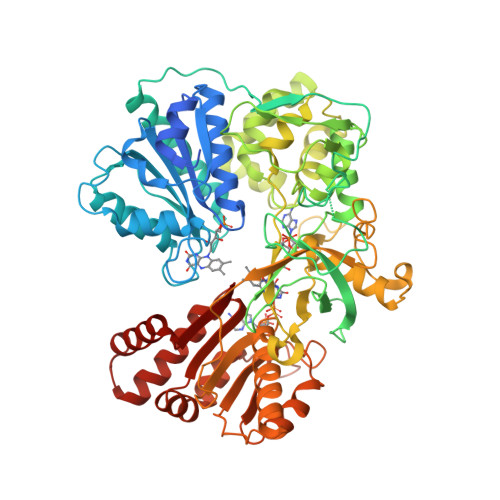
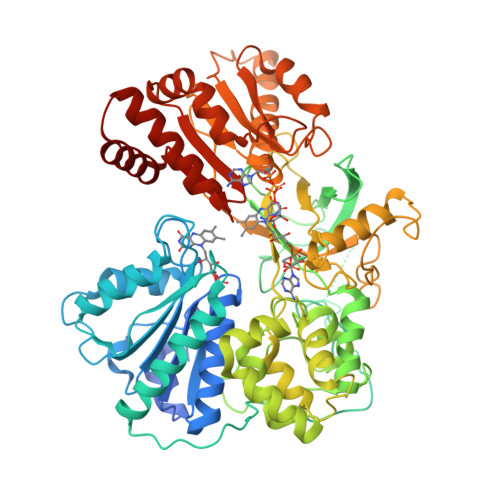
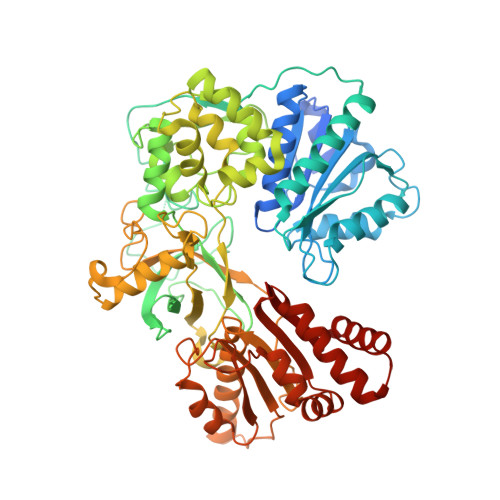
NADPH-cytochrome P450 reductase transfers two reducing equivalents derived from a hydride ion of NADPH via FAD and FMN to the large family of microsomal cytochrome P450 monooxygenases in one-electron transfer steps. The mechanism of electron transfer by diflavin reductases remains elusive and controversial. Here, we determined the crystal structure of truncated yeast NADPH-cytochrome P450 reductase, which is functionally active toward its physiological substrate cytochrome P450, and discovered a second FMN binding site at the interface of the connecting and FMN binding domains. The two FMN binding sites have different accessibilities to the bulk solvent and different amino acid environments, suggesting stabilization of different electronic structures of the reduced flavin. Since only one FMN cofactor is required for function, a hypothetical mechanism of electron transfer is discussed that proposes shuttling of a single FMN between these two sites coupled with the transition between two semiquinone forms, neutral (blue) and anionic (red).
Organizational Affiliation:
Wolfson Laboratory of P450 Biodiversity, Swansea Medical School University of Wales Swansea, Swansea, Wales SA2 8PP, UK.