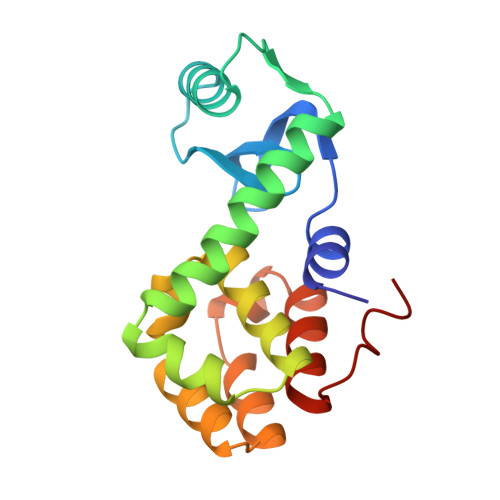
Structure of bacteriophage T4 lysozyme refined at 1.7 A resolution.
Weaver, L.H., Matthews, B.W.(1987) J Mol Biol 193: 189-199
- PubMed: 3586019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/0022-2836(87)90636-x
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
2LZM - PubMed Abstract:
The structure of the lysozyme from bacteriophage T4 has been refined at 1.7 A resolution to a crystallographic residual of 19.3%. The final model has bond lengths and bond angles that differ from "ideal" values by 0.019 A and 2.7 degrees, respectively. The crystals are grown from electron-dense phosphate solutions and the use of an appropriate solvent continuum substantially improved the agreement between the observed and calculated structure factors at low resolution. Apart from changes in the conformations of some side-chains, the refinement confirms the structure of the molecule as initially derived from a 2.4 A resolution electron density map. There are 118 well-ordered solvent molecules that are associated with the T4 lysozyme molecule in the crystal. Four of these are more-or-less buried. There is a clustering of water molecules within the active site cleft but, other than this, the solvent molecules are dispersed around the surface of the molecule and do not aggregate into ice-like structures or pentagonal or hexagonal clusters. The apparent motion of T4 lysozyme in the crystal can be interpreted in terms of significant interdomain motion corresponding to an opening and closing of the active site cleft. For the amino-terminal domain the motion can be described equally well (correlation coefficients approx. 0.87) as quasi-rigid-body motion either about a point or about an axis of rotation. The motion in the crystals of the carboxy-terminal domain is best described as rotation about an axis (correlation coefficient 0.80) although in this case the apparent motion seems to be influenced in part by crystal contacts and may be of questionable relevance to dynamics in solution.