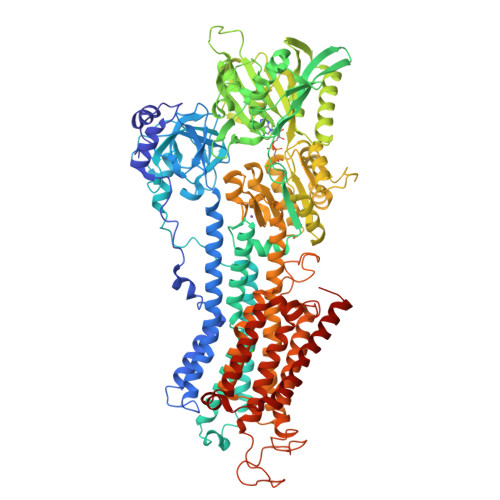
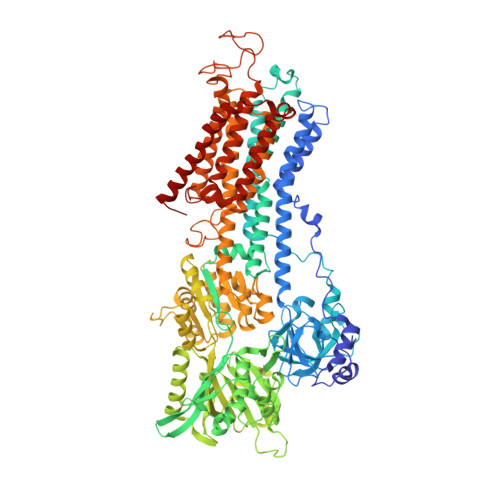
Ion pathways in the sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca2+-ATPase.
Bublitz, M., Musgaard, M., Poulsen, H., Thogersen, L., Olesen, C., Schiott, B., Morth, J.P., Moller, J.V., Nissen, P.(2013) J Biological Chem 288: 10759-10765
- PubMed: 23400778
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.R112.436550
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
3N5K, 3N8G - PubMed Abstract:
The sarco/endoplasmic reticulum Ca(2+)-ATPase (SERCA) is a transmembrane ion transporter belonging to the P(II)-type ATPase family. It performs the vital task of re-sequestering cytoplasmic Ca(2+) to the sarco/endoplasmic reticulum store, thereby also terminating Ca(2+)-induced signaling such as in muscle contraction. This minireview focuses on the transport pathways of Ca(2+) and H(+) ions across the lipid bilayer through SERCA. The ion-binding sites of SERCA are accessible from either the cytoplasm or the sarco/endoplasmic reticulum lumen, and the Ca(2+) entry and exit channels are both formed mainly by rearrangements of four N-terminal transmembrane α-helices. Recent improvements in the resolution of the crystal structures of rabbit SERCA1a have revealed a hydrated pathway in the C-terminal transmembrane region leading from the ion-binding sites to the cytosol. A comparison of different SERCA conformations reveals that this C-terminal pathway is exclusive to Ca(2+)-free E2 states, suggesting that it may play a functional role in proton release from the ion-binding sites. This is in agreement with molecular dynamics simulations and mutational studies and is in striking analogy to a similar pathway recently described for the related sodium pump. We therefore suggest a model for the ion exchange mechanism in P(II)-ATPases including not one, but two cytoplasmic pathways working in concert.
Organizational Affiliation:
Centre for Membrane Pumps in Cells and Disease (PUMPkin), Aarhus University, DK-8000 Aarhus C, Denmark.