Discovery of novel N-phenylphenoxyacetamide derivatives as EthR inhibitors and ethionamide boosters by combining high-throughput screening and synthesis.
Flipo, M., Willand, N., Lecat-Guillet, N., Hounsou, C., Desroses, M., Leroux, F., Lens, Z., Villeret, V., Wohlkonig, A., Wintjens, R., Christophe, T., Kyoung Jeon, H., Locht, C., Brodin, P., Baulard, A.R., Deprez, B.(2012) J Med Chem 55: 6391-6402
- PubMed: 22738293
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/jm300377g
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
4DW6 - PubMed Abstract:
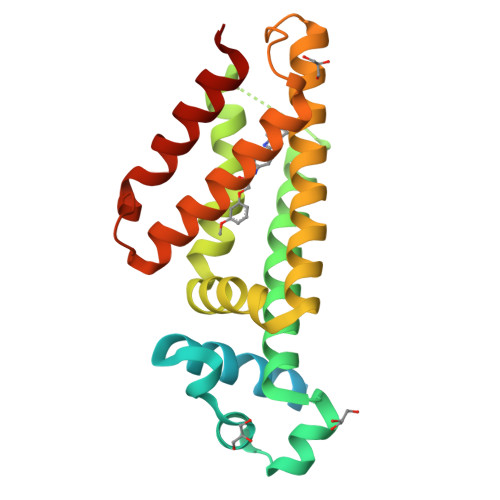
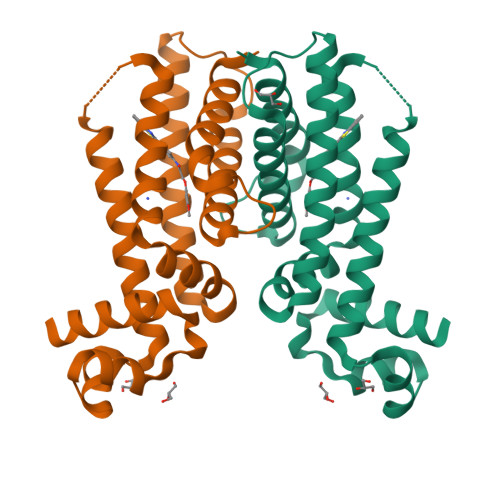
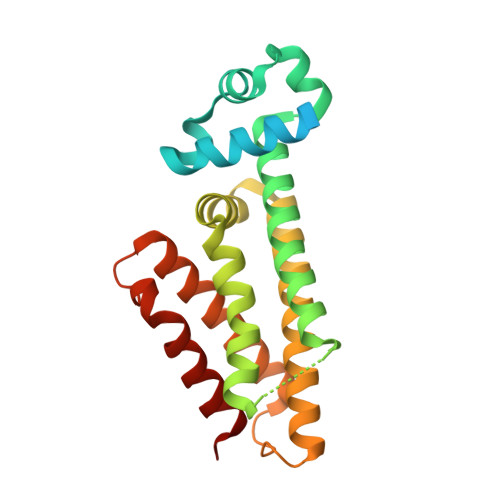
In this paper, we describe the screening of a 14640-compound library using a novel whole mycobacteria phenotypic assay to discover inhibitors of EthR, a transcriptional repressor implicated in the innate resistance of Mycobacterium tuberculosis to the second-line antituberculosis drug ethionamide. From this screening a new chemical family of EthR inhibitors bearing an N-phenylphenoxyacetamide motif was identified. The X-ray structure of the most potent compound crystallized with EthR inspired the synthesis of a 960-member focused library. These compounds were tested in vitro using a rapid thermal shift assay on EthR to accelerate the optimization. The best compounds were synthesized on a larger scale and confirmed as potent ethionamide boosters on M. tuberculosis -infected macrophages. Finally, the cocrystallization of the best optimized analogue with EthR revealed an unexpected reorientation of the ligand in the binding pocket.
Organizational Affiliation:
Université Lille Nord de France, F-59000 Lille, France.