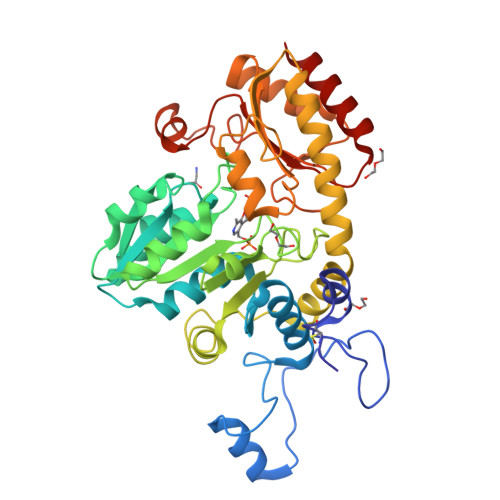
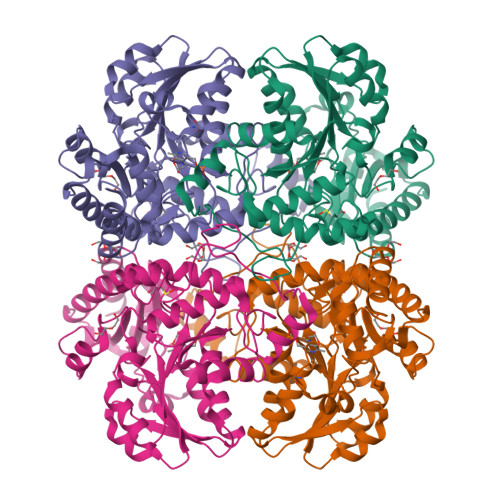
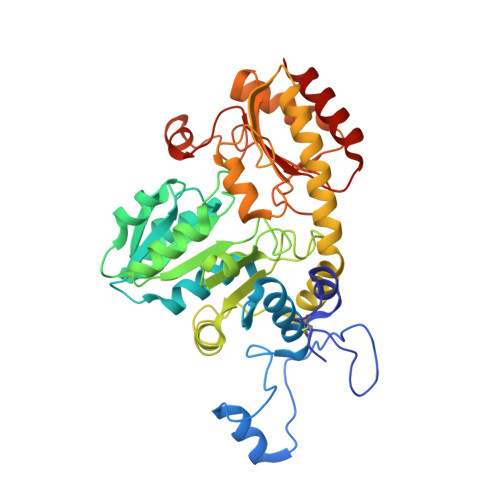
Crystal structure of the external aldimine of Citrobacter freundii methionine gamma-lyase with glycine provides insight in mechanisms of two stages of physiological reaction and isotope exchange of alpha- and beta-protons of competitive inhibitors.
Revtovich, S.V., Faleev, N.G., Morozova, E.A., Anufrieva, N.V., Nikulin, A.D., Demidkina, T.V.(2014) Biochimie 101: 161-167
- PubMed: 24463191
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biochi.2014.01.007
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
4HF8 - PubMed Abstract:
The three-dimensional structure of the external aldimine of Citrobacter freundii methionine γ-lyase with competitive inhibitor glycine has been determined at 2.45 Å resolution. It revealed subtle conformational changes providing effective binding of the inhibitor and facilitating labilization of Cα-protons of the external aldimine. The structure shows that 1, 3-prototropic shift of Cα-proton to C4'-atom of the cofactor may proceed with participation of active site Lys210 residue whose location is favorable for performing this transformation by a concerted mechanism. The observed stereoselectivity of isotopic exchange of enantiotopic Cα-protons of glycine may be explained on the basis of external aldimine structure. The exchange of Cα-pro-(R)-proton of the external aldimine might proceed in the course of the concerted transfer of the proton from Cα-atom of glycine to C4'-atom of the cofactor. The exchange of Cα-pro-(S)-proton may be performed with participation of Tyr113 residue which should be present in its basic form. The isotopic exchange of β-protons, which is observed for amino acids bearing longer side groups, may be effected by two catalytic groups: Lys210 in its basic form, and Tyr113 acting as a general acid.
Organizational Affiliation:
Engelhardt Institute of Molecular Biology, Russian Academy of Sciences, Vavilov Str. 32, Moscow 119991, Russia.