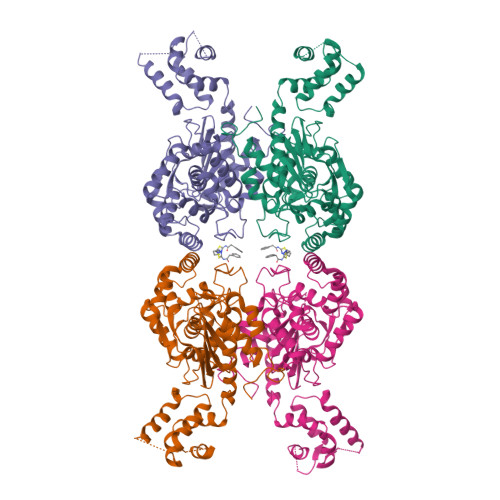
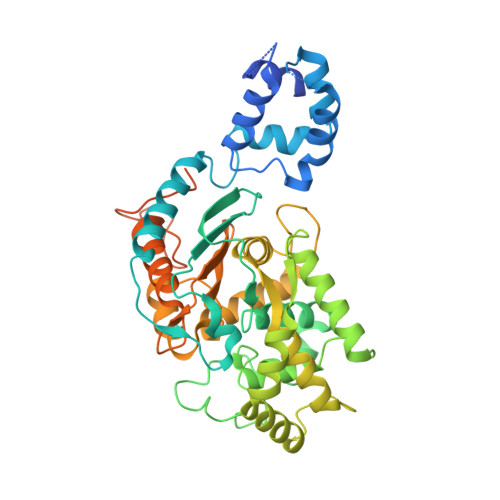
Active Glutaminase C Self-assembles into a Supratetrameric Oligomer That Can Be Disrupted by an Allosteric Inhibitor.
Ferreira, A.P., Cassago, A., Goncalves Kde, A., Dias, M.M., Adamoski, D., Ascencao, C.F., Honorato, R.V., de Oliveira, J.F., Ferreira, I.M., Fornezari, C., Bettini, J., Oliveira, P.S., Paes Leme, A.F., Portugal, R.V., Ambrosio, A.L., Dias, S.M.(2013) J Biological Chem 288: 28009-28020
- PubMed: 23935106
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M113.501346
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
4JKT - PubMed Abstract:
The phosphate-dependent transition between enzymatically inert dimers into catalytically capable tetramers has long been the accepted mechanism for the glutaminase activation. Here, we demonstrate that activated glutaminase C (GAC) self-assembles into a helical, fiber-like double-stranded oligomer and propose a molecular model consisting of seven tetramer copies per turn per strand interacting via the N-terminal domains. The loop (321)LRFNKL(326) is projected as the major regulating element for self-assembly and enzyme activation. Furthermore, the previously identified in vivo lysine acetylation (Lys(311) in humans, Lys(316) in mouse) is here proposed as an important down-regulator of superoligomer assembly and protein activation. Bis-2-(5-phenylacetamido-1,3,4-thiadiazol-2-yl)ethyl sulfide, a known glutaminase inhibitor, completely disrupted the higher order oligomer, explaining its allosteric mechanism of inhibition via tetramer stabilization. A direct correlation between the tendency to self-assemble and the activity levels of the three mammalian glutaminase isozymes was established, with GAC being the most active enzyme while forming the longest structures. Lastly, the ectopic expression of a fiber-prone superactive GAC mutant in MDA-MB 231 cancer cells provided considerable proliferative advantages to transformed cells. These findings yield unique implications for the development of GAC-oriented therapeutics targeting tumor metabolism.
Organizational Affiliation:
From the Laboratórios Nacionais de Biociências e.