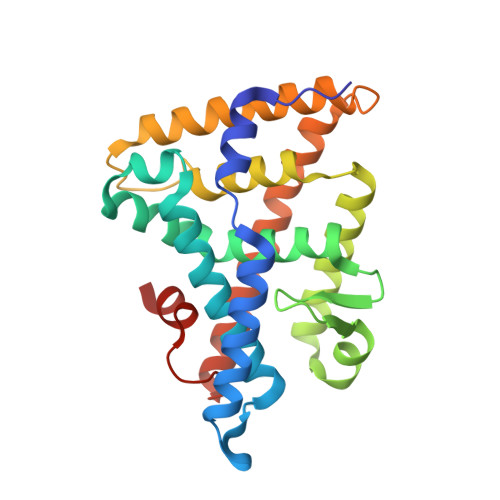
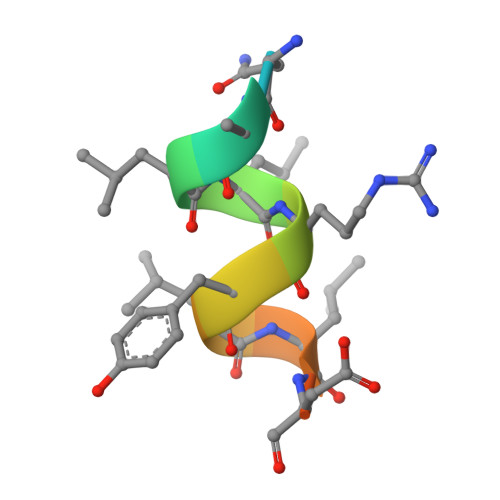
Unexpected Allosteric Network Contributes to LRH-1 Co-regulator Selectivity.
Musille, P.M., Kossmann, B.R., Kohn, J.A., Ivanov, I., Ortlund, E.A.(2016) J Biol Chem 291: 1411-1426
- PubMed: 26553876
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M115.662874
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
4PLD, 4PLE - PubMed Abstract:
Phospholipids (PLs) are unusual signaling hormones sensed by the nuclear receptor liver receptor homolog-1 (LRH-1), which has evolved a novel allosteric pathway to support appropriate interaction with co-regulators depending on ligand status. LRH-1 plays an important role in controlling lipid and cholesterol homeostasis and is a potential target for the treatment of metabolic and neoplastic diseases. Although the prospect of modulating LRH-1 via small molecules is exciting, the molecular mechanism linking PL structure to transcriptional co-regulator preference is unknown. Previous studies showed that binding to an activating PL ligand, such as dilauroylphosphatidylcholine, favors LRH-1's interaction with transcriptional co-activators to up-regulate gene expression. Both crystallographic and solution-based structural studies showed that dilauroylphosphatidylcholine binding drives unanticipated structural fluctuations outside of the canonical activation surface in an alternate activation function (AF) region, encompassing the β-sheet-H6 region of the protein. However, the mechanism by which dynamics in the alternate AF influences co-regulator selectivity remains elusive. Here, we pair x-ray crystallography with molecular modeling to identify an unexpected allosteric network that traverses the protein ligand binding pocket and links these two elements to dictate selectivity. We show that communication between the alternate AF region and classical AF2 is correlated with the strength of the co-regulator interaction. This work offers the first glimpse into the conformational dynamics that drive this unusual PL-mediated nuclear hormone receptor activation.
Organizational Affiliation:
From the Department of Biochemistry, Emory University School of Medicine, Atlanta, Georgia 30322 and.