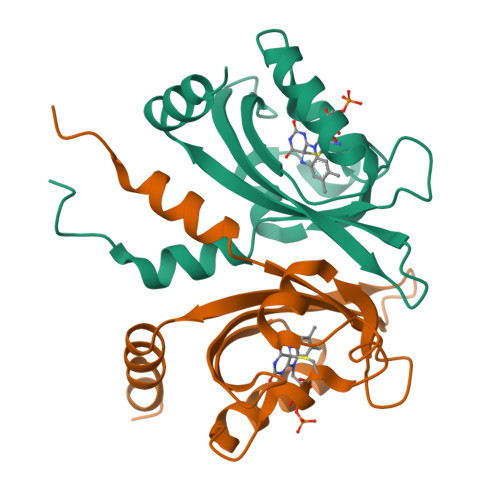
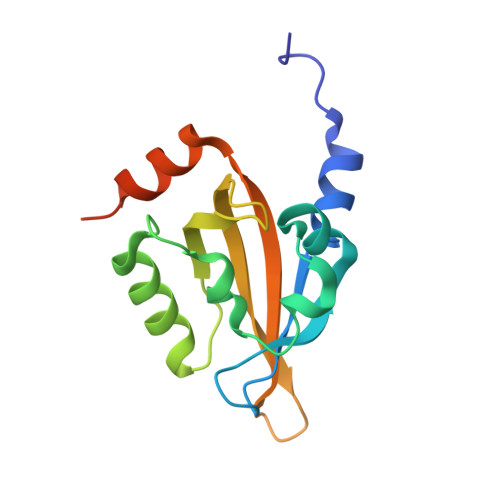
Blue light-induced LOV domain dimerization enhances the affinity of Aureochrome 1a for its target DNA sequence.
Heintz, U., Schlichting, I.(2016) Elife 5: e11860-e11860
- PubMed: 26754770
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.11860
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
5DKK, 5DKL - PubMed Abstract:
The design of synthetic optogenetic tools that allow precise spatiotemporal control of biological processes previously inaccessible to optogenetic control has developed rapidly over the last years. Rational design of such tools requires detailed knowledge of allosteric light signaling in natural photoreceptors. To understand allosteric communication between sensor and effector domains, characterization of all relevant signaling states is required. Here, we describe the mechanism of light-dependent DNA binding of the light-oxygen-voltage (LOV) transcription factor Aureochrome 1a from Phaeodactylum tricornutum (PtAu1a) and present crystal structures of a dark state LOV monomer and a fully light-adapted LOV dimer. In combination with hydrogen/deuterium-exchange, solution scattering data and DNA-binding experiments, our studies reveal a light-sensitive interaction between the LOV and basic region leucine zipper DNA-binding domain that together with LOV dimerization results in modulation of the DNA affinity of PtAu1a. We discuss the implications of these results for the design of synthetic LOV-based photosensors with application in optogenetics.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Biomolecular Mechanisms, Max Planck Institute for Medical Research, Heidelberg, Germany.