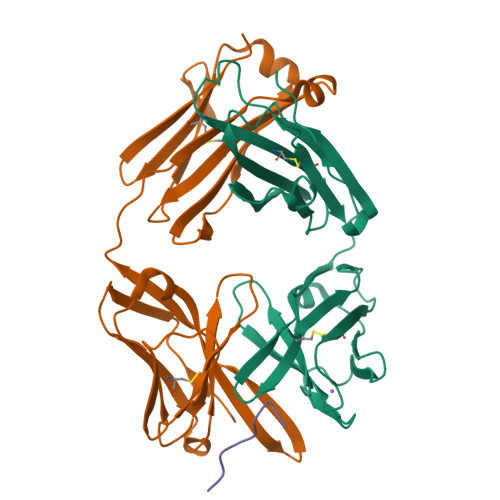
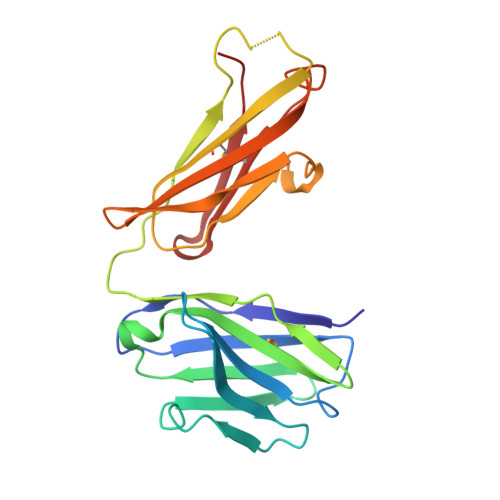
Linear Epitopes in Vaccinia Virus A27 Are Targets of Protective Antibodies Induced by Vaccination against Smallpox.
Kaever, T., Matho, M.H., Meng, X., Crickard, L., Schlossman, A., Xiang, Y., Crotty, S., Peters, B., Zajonc, D.M.(2016) J Virol 90: 4334-4345
- PubMed: 26889021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1128/JVI.02878-15
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
5EOQ, 5EOR - PubMed Abstract:
Vaccinia virus (VACV) A27 is a target for viral neutralization and part of the Dryvax smallpox vaccine. A27 is one of the three glycosaminoglycan (GAG) adhesion molecules and binds to heparan sulfate. To understand the function of anti-A27 antibodies, especially their protective capacity and their interaction with A27, we generated and subsequently characterized 7 murine monoclonal antibodies (MAbs), which fell into 4 distinct epitope groups (groups I to IV). The MAbs in three groups (groups I, III, and IV) bound to linear peptides, while the MAbs in group II bound only to VACV lysate and recombinant A27, suggesting that they recognized a conformational and discontinuous epitope. Only group I antibodies neutralized the mature virion in a complement-dependent manner and protected against VACV challenge, while a group II MAb partially protected against VACV challenge but did not neutralize the mature virion. The epitope for group I MAbs was mapped to a region adjacent to the GAG binding site, a finding which suggests that group I MAbs could potentially interfere with the cellular adhesion of A27. We further determined the crystal structure of the neutralizing group I MAb 1G6, as well as the nonneutralizing group IV MAb 8E3, bound to the corresponding linear epitope-containing peptides. Both the light and the heavy chains of the antibodies are important in binding to their antigens. For both antibodies, the L1 loop seems to dominate the overall polar interactions with the antigen, while for MAb 8E3, the light chain generally appears to make more contacts with the antigen. Vaccinia virus is a powerful model to study antibody responses upon vaccination, since its use as the smallpox vaccine led to the eradication of one of the world's greatest killers. The immunodominant antigens that elicit the protective antibodies are known, yet for many of these antigens, little information about their precise interaction with antibodies is available. In an attempt to better understand the interplay between the antibodies and their antigens, we generated and functionally characterized a panel of anti-A27 antibodies and studied their interaction with the epitope using X-ray crystallography. We identified one protective antibody that binds adjacent to the heparan sulfate binding site of A27, likely affecting ligand binding. Analysis of the antibody-antigen interaction supports a model in which antibodies that can interfere with the functional activity of the antigen are more likely to confer protection than those that bind at the extremities of the antigen.
Organizational Affiliation:
Division of Vaccine Discovery, La Jolla Institute for Allergy and Immunology (LJI), La Jolla, California, USA.