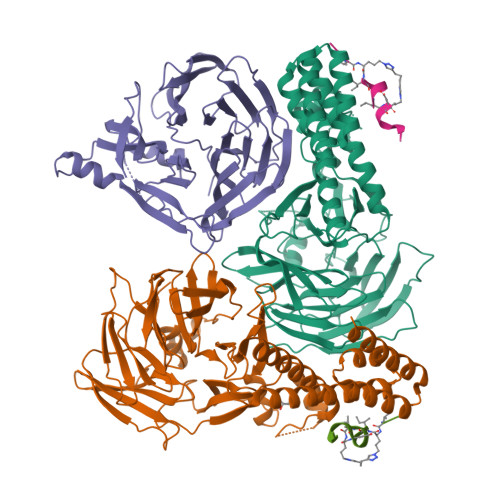
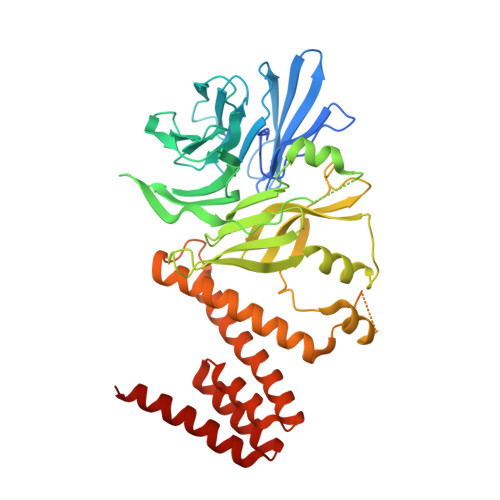
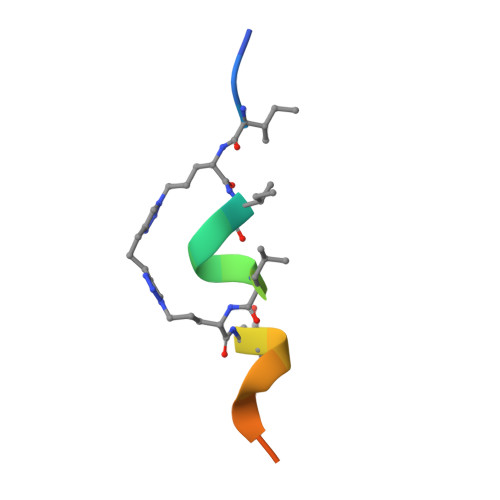
Targeting the Genome-Stability Hub Ctf4 by Stapled-Peptide Design.
Wu, Y., Villa, F., Maman, J., Lau, Y.H., Dobnikar, L., Simon, A.C., Labib, K., Spring, D.R., Pellegrini, L.(2017) Angew Chem Int Ed Engl 56: 12866-12872
- PubMed: 28815832
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.201705611
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
5NXQ - PubMed Abstract:
The exploitation of synthetic lethality by small-molecule targeting of pathways that maintain genomic stability is an attractive chemotherapeutic approach. The Ctf4/AND-1 protein hub, which links DNA replication, repair, and chromosome segregation, represents a novel target for the synthetic lethality approach. Herein, we report the design, optimization, and validation of double-click stapled peptides encoding the Ctf4-interacting peptide (CIP) of the replicative helicase subunit Sld5. By screening stapling positions in the Sld5 CIP, we identified an unorthodox i,i+6 stapled peptide with improved, submicromolar binding to Ctf4. The mode of interaction with Ctf4 was confirmed by a crystal structure of the stapled Sld5 peptide bound to Ctf4. The stapled Sld5 peptide was able to displace the Ctf4 partner DNA polymerase α from the replisome in yeast extracts. Our study provides proof-of-principle evidence for the development of small-molecule inhibitors of the human CTF4 orthologue AND-1.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Chemistry, University of Cambridge, Cambridge, CB2 1EW, UK.