How the glycosyltransferase OGT catalyzes amide bond cleavage.
Janetzko, J., Trauger, S.A., Lazarus, M.B., Walker, S.(2016) Nat Chem Biol 12: 899-901
- PubMed: 27618188
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nchembio.2173
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
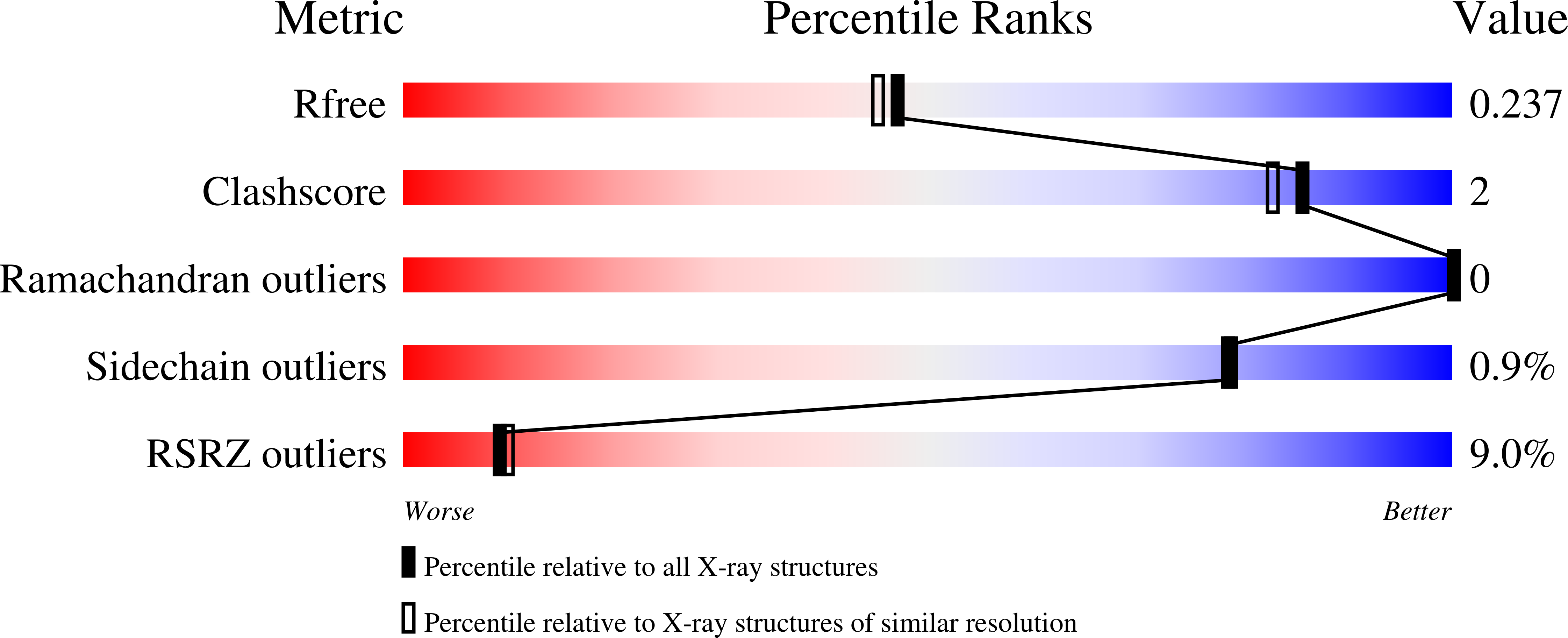
5HGV - PubMed Abstract:
The essential human enzyme O-linked β-N-acetylglucosamine transferase (OGT), known for modulating the functions of nuclear and cytoplasmic proteins through serine and threonine glycosylation, was unexpectedly implicated in the proteolytic maturation of the cell cycle regulator host cell factor-1 (HCF-1). Here we show that HCF-1 cleavage occurs via glycosylation of a glutamate side chain followed by on-enzyme formation of an internal pyroglutamate, which undergoes spontaneous backbone hydrolysis.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Chemistry and Chemical Biology, Harvard University, Cambridge, Massachusetts, USA.