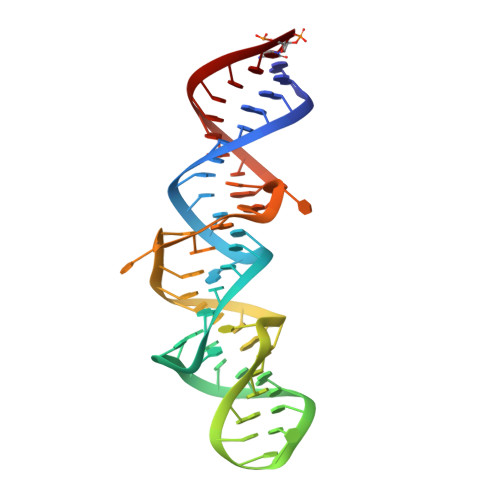
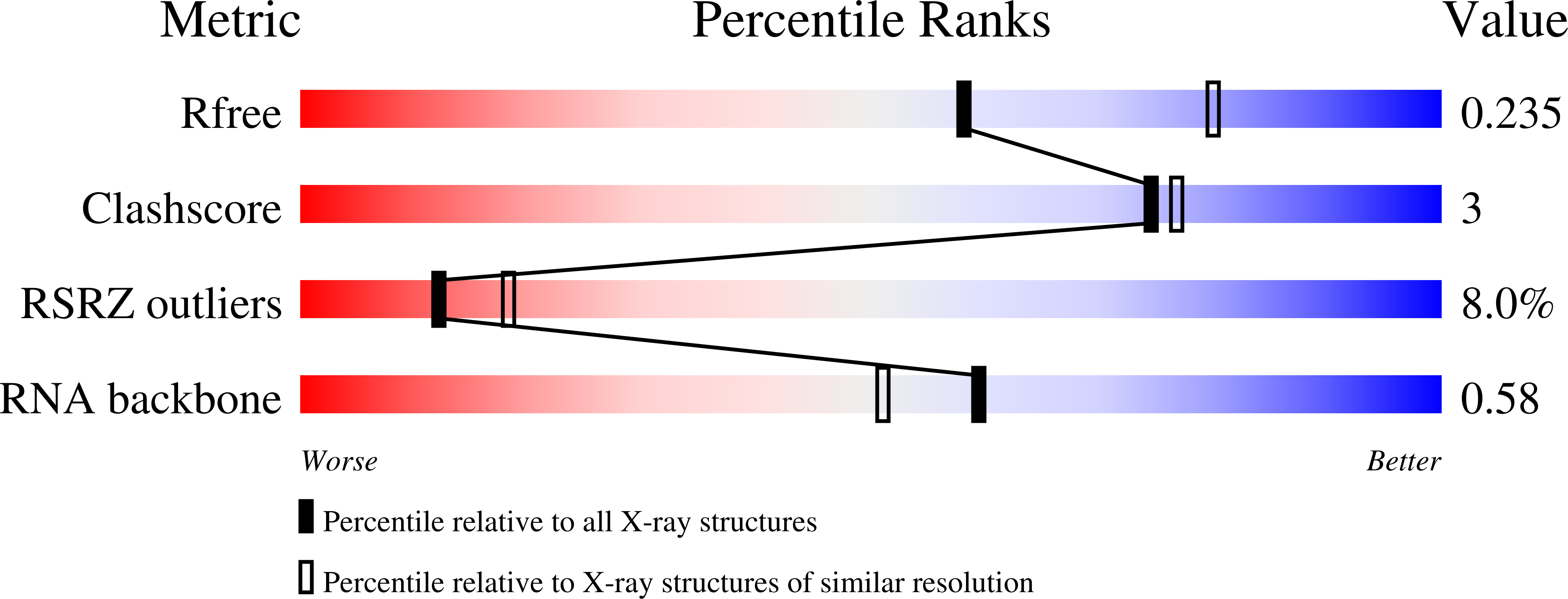The crystal structure of the 5 functional domain of the transcription riboregulator 7SK.
Martinez-Zapien, D., Legrand, P., McEwen, A.G., Proux, F., Cragnolini, T., Pasquali, S., Dock-Bregeon, A.C.(2017) Nucleic Acids Res 45: 3568-3579
- PubMed: 28082395
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkw1351
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
5LYS, 5LYU, 5LYV - PubMed Abstract:
In vertebrates, the 7SK RNA forms the scaffold of a complex, which regulates transcription pausing of RNA-polymerase II. By binding to the HEXIM protein, the complex comprising proteins LARP7 and MePCE captures the positive transcription elongation factor P-TEFb and prevents phosphorylation of pausing factors. The HEXIM-binding site embedded in the 5΄-hairpin of 7SK (HP1) encompasses a short signature sequence, a GAUC repeat framed by single-stranded uridines. The present crystal structure of HP1 shows a remarkably straight helical stack involving several unexpected triples formed at a central region. Surprisingly, two uridines of the signature sequence make triple interactions in the major groove of the (GAUC)2. The third uridine is turned outwards or inward, wedging between the other uridines, thus filling the major groove. A molecular dynamics simulation indicates that these two conformations of the signature sequence represent stable alternatives. Analyses of the interaction with the HEXIM protein confirm the importance of the triple interactions at the signature sequence. Altogether, the present structural analysis of 7SK HP1 highlights an original mechanism of swapping bases, which could represent a possible '7SK signature' and provides new insight into the functional importance of the plasticity of RNA.
Organizational Affiliation:
Biotechnologie et signalisation cellulaire, CNRS UMR 7242, Ecole Supérieure de Biotechnologie de Strasbourg, F-67412 Illkirch, France.