Dioxygen Sensitivity of [Fe]-Hydrogenase in the Presence of Reducing Substrates.
Huang, G., Wagner, T., Ermler, U., Bill, E., Ataka, K., Shima, S.(2018) Angew Chem Int Ed Engl 57: 4917-4920
- PubMed: 29462510
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.201712293
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
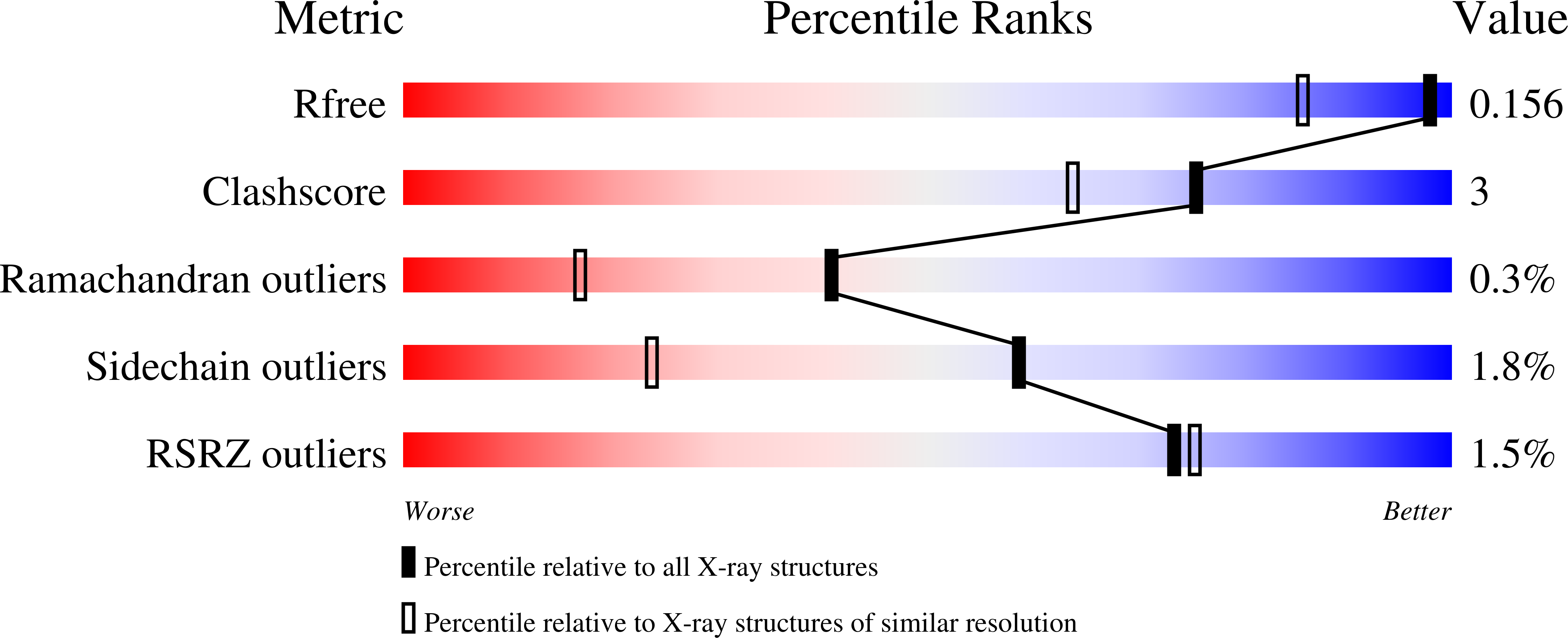
5OK4 - PubMed Abstract:
Mono-iron hydrogenase ([Fe]-hydrogenase) reversibly catalyzes the transfer of a hydride ion from H 2 to methenyltetrahydromethanopterin (methenyl-H 4 MPT + ) to form methylene-H 4 MPT. Its iron guanylylpyridinol (FeGP) cofactor plays a key role in H 2 activation. Evidence is presented for O 2 sensitivity of [Fe]-hydrogenase under turnover conditions in the presence of reducing substrates, methylene-H 4 MPT or methenyl-H 4 MPT + /H 2 . Only then, H 2 O 2 is generated, which decomposes the FeGP cofactor; as demonstrated by spectroscopic analyses and the crystal structure of the deactivated enzyme. O 2 reduction to H 2 O 2 requires a reductant, which can be a catalytic intermediate transiently formed during the [Fe]-hydrogenase reaction. The most probable candidate is an iron hydride species; its presence has already been predicted by theoretical studies of the catalytic reaction. The findings support predictions because the same type of reduction reaction is described for ruthenium hydride complexes that hydrogenate polar compounds.
Organizational Affiliation:
Max-Planck-Institut für terrestrische Mikrobiologie, Karl-von-Frisch-Straße 10, 35043, Marburg, Germany.