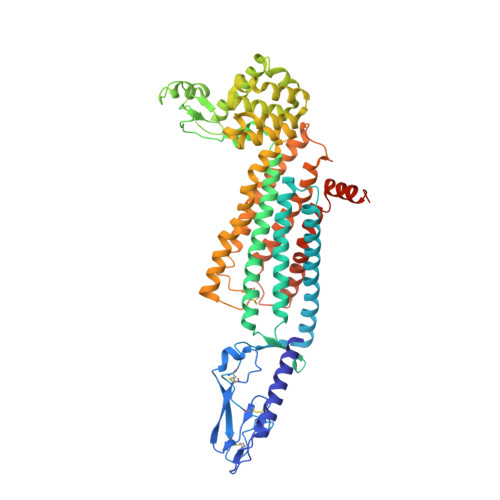
Structure of the full-length glucagon class B G-protein-coupled receptor.
Zhang, H., Qiao, A., Yang, D., Yang, L., Dai, A., de Graaf, C., Reedtz-Runge, S., Dharmarajan, V., Zhang, H., Han, G.W., Grant, T.D., Sierra, R.G., Weierstall, U., Nelson, G., Liu, W., Wu, Y., Ma, L., Cai, X., Lin, G., Wu, X., Geng, Z., Dong, Y., Song, G., Griffin, P.R., Lau, J., Cherezov, V., Yang, H., Hanson, M.A., Stevens, R.C., Zhao, Q., Jiang, H., Wang, M.W., Wu, B.(2017) Nature 546: 259-264
- PubMed: 28514451
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nature22363
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
5XEZ, 5XF1 - PubMed Abstract:
The human glucagon receptor, GCGR, belongs to the class B G-protein-coupled receptor family and plays a key role in glucose homeostasis and the pathophysiology of type 2 diabetes. Here we report the 3.0 Å crystal structure of full-length GCGR containing both the extracellular domain and transmembrane domain in an inactive conformation. The two domains are connected by a 12-residue segment termed the stalk, which adopts a β-strand conformation, instead of forming an α-helix as observed in the previously solved structure of the GCGR transmembrane domain. The first extracellular loop exhibits a β-hairpin conformation and interacts with the stalk to form a compact β-sheet structure. Hydrogen-deuterium exchange, disulfide crosslinking and molecular dynamics studies suggest that the stalk and the first extracellular loop have critical roles in modulating peptide ligand binding and receptor activation. These insights into the full-length GCGR structure deepen our understanding of the signalling mechanisms of class B G-protein-coupled receptors.
Organizational Affiliation:
CAS Key Laboratory of Receptor Research, Shanghai Institute of Materia Medica, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 555 Zuchongzhi Road, Pudong, Shanghai 201203, China.