Structure and Functional Binding Epitope of V-domain Ig Suppressor of T Cell Activation.
Mehta, N., Maddineni, S., Mathews, I.I., Andres Parra Sperberg, R., Huang, P.S., Cochran, J.R.(2019) Cell Rep 28: 2509-2516.e5
- PubMed: 31484064
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2019.07.073
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
6OIL - PubMed Abstract:
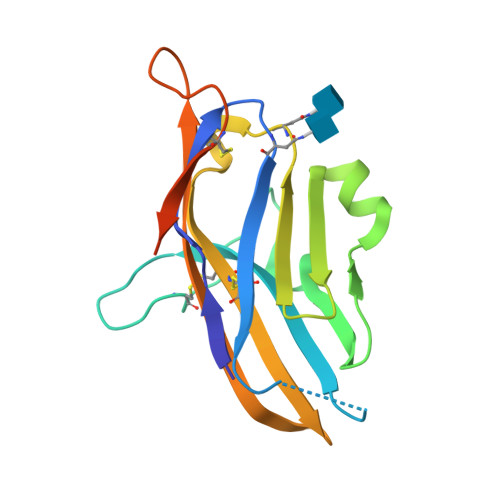
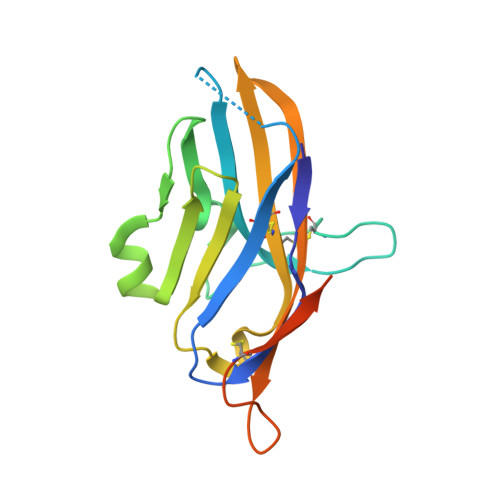
V-domain immunoglobulin (Ig) suppressor of T cell activation (VISTA) is an immune checkpoint protein that inhibits the T cell response against cancer. Similar to PD-1 and CTLA-4, a blockade of VISTA promotes tumor clearance by the immune system. Here, we report a 1.85 Å crystal structure of the elusive human VISTA extracellular domain, whose lack of homology necessitated a combinatorial MR-Rosetta approach for structure determination. We highlight features that make the VISTA immunoglobulin variable (IgV)-like fold unique among B7 family members, including two additional disulfide bonds and an extended loop region with an attached helix that we show forms a contiguous binding epitope for a clinically relevant anti-VISTA antibody. We propose an overlap of this antibody-binding region with the binding epitope for V-set and Ig domain containing 3 (VSIG3), a purported functional binding partner of VISTA. The structure and functional epitope presented here will help guide future drug development efforts against this important checkpoint target.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Bioengineering, Stanford University, Stanford, CA 94305, USA.