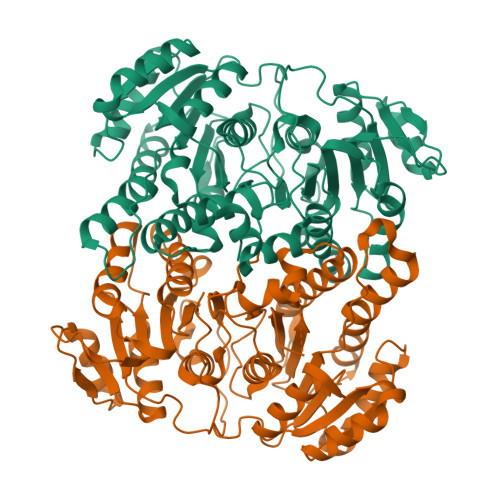
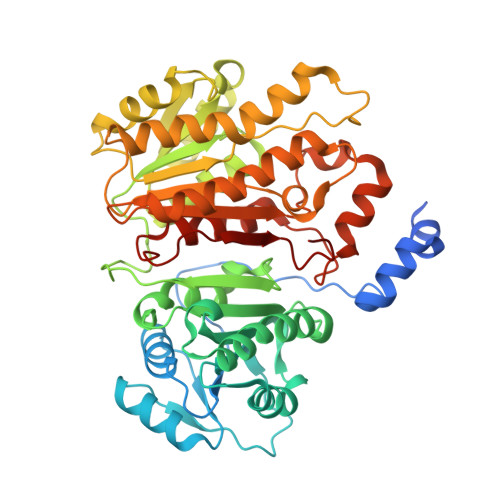
Insights into Acinetobacter baumannii fatty acid synthesis 3-oxoacyl-ACP reductases.
Cross, E.M., Adams, F.G., Waters, J.K., Aragao, D., Eijkelkamp, B.A., Forwood, J.K.(2021) Sci Rep 11: 7050-7050
- PubMed: 33782435
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-021-86400-1
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
6NRP, 6UDS, 6UUT, 6UUV, 6WPR - PubMed Abstract:
Treatments for 'superbug' infections are the focus for innovative research, as drug resistance threatens human health and medical practices globally. In particular, Acinetobacter baumannii (Ab) infections are repeatedly reported as difficult to treat due to increasing antibiotic resistance. Therefore, there is increasing need to identify novel targets in the development of different antimicrobials. Of particular interest is fatty acid synthesis, vital for the formation of phospholipids, lipopolysaccharides/lipooligosaccharides, and lipoproteins of Gram-negative envelopes. The bacterial type II fatty acid synthesis (FASII) pathway is an attractive target for the development of inhibitors and is particularly favourable due to the differences from mammalian type I fatty acid synthesis. Discrete enzymes in this pathway include two reductase enzymes: 3-oxoacyl-acyl carrier protein (ACP) reductase (FabG) and enoyl-ACP reductase (FabI). Here, we investigate annotated FabG homologs, finding a low-molecular weight 3-oxoacyl-ACP reductase, as the most likely FASII FabG candidate, and high-molecular weight 3-oxoacyl-ACP reductase (HMwFabG), showing differences in structure and coenzyme preference. To date, this is the second bacterial high-molecular weight FabG structurally characterized, following FabG4 from Mycobacterium. We show that ΔAbHMwfabG is impaired for growth in nutrient rich media and pellicle formation. We also modelled a third 3-oxoacyl-ACP reductase, which we annotated as AbSDR. Despite containing residues for catalysis and the ACP coordinating motif, biochemical analyses showed limited activity against an acetoacetyl-CoA substrate in vitro. Inhibitors designed to target FabG proteins and thus prevent fatty acid synthesis may provide a platform for use against multidrug-resistant pathogens including A. baumannii.
Organizational Affiliation:
School of Biomedical Sciences, Charles Sturt University, Wagga Wagga, NSW, 2678, Australia.