Structure of the Human cGAS-DNA Complex Reveals Enhanced Control of Immune Surveillance.
Zhou, W., Whiteley, A.T., de Oliveira Mann, C.C., Morehouse, B.R., Nowak, R.P., Fischer, E.S., Gray, N.S., Mekalanos, J.J., Kranzusch, P.J.(2018) Cell 174: 300-311.e11
- PubMed: 30007416
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2018.06.026
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
6CT9, 6CTA - PubMed Abstract:
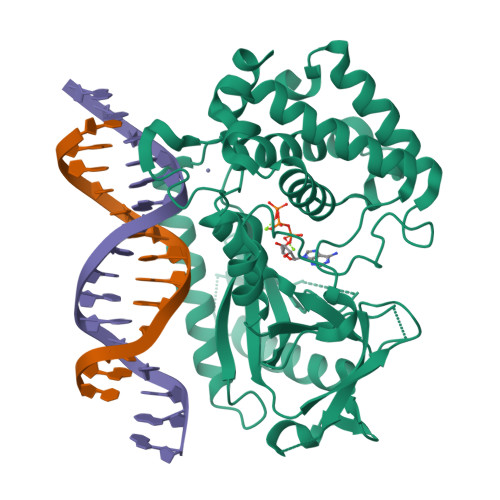
Cyclic GMP-AMP synthase (cGAS) recognition of cytosolic DNA is critical for immune responses to pathogen replication, cellular stress, and cancer. Existing structures of the mouse cGAS-DNA complex provide a model for enzyme activation but do not explain why human cGAS exhibits severely reduced levels of cyclic GMP-AMP (cGAMP) synthesis compared to other mammals. Here, we discover that enhanced DNA-length specificity restrains human cGAS activation. Using reconstitution of cGAMP signaling in bacteria, we mapped the determinant of human cGAS regulation to two amino acid substitutions in the DNA-binding surface. Human-specific substitutions are necessary and sufficient to direct preferential detection of long DNA. Crystal structures reveal why removal of human substitutions relaxes DNA-length specificity and explain how human-specific DNA interactions favor cGAS oligomerization. These results define how DNA-sensing in humans adapted for enhanced specificity and provide a model of the active human cGAS-DNA complex to enable structure-guided design of cGAS therapeutics.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Microbiology and Immunobiology, Harvard Medical School, Boston, MA 02115, USA; Department of Cancer Immunology and Virology, Dana-Farber Cancer Institute, Boston, MA 02115, USA.