Structural Basis for Inhibition of ROS-Producing Respiratory Complex I by NADH-OH.
Friedrich, T., Vranas, M., Wohlwend, D., Qiu, D., Gerhardt, S., Trncik, C., Pervaiz, M., Ritter, K., Steimle, S., Randazzo, A., Einsle, O., Gunther, S., Jessen, H.J., Kotlyar, A.(2021) Angew Chem Int Ed Engl
- PubMed: 34612584
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.202112165
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
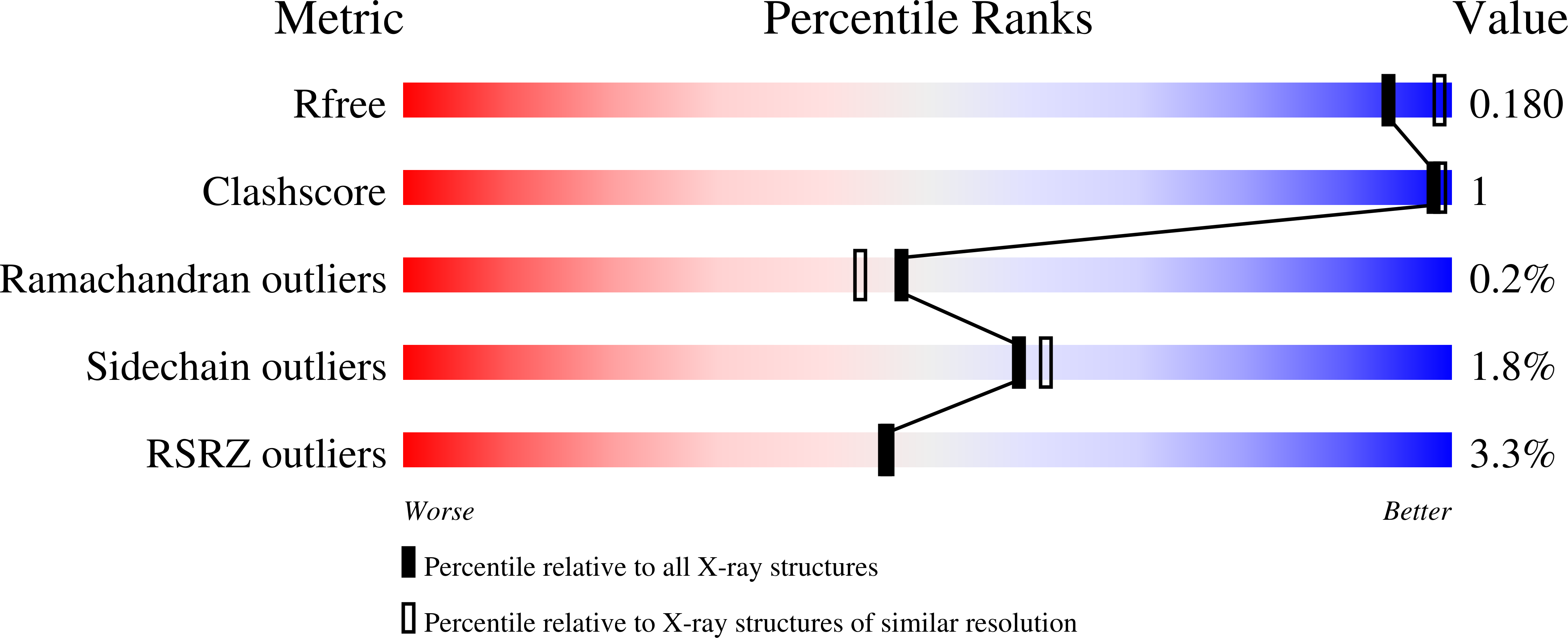
6SAQ - PubMed Abstract:
NADH:ubiquinone oxidoreductase, respiratory complex I, plays a central role in cellular energy metabolism. As a major source of reactive oxygen species (ROS) it affects ageing and mitochondrial dysfunction. The novel inhibitor NADH-OH specifically blocks NADH oxidation and ROS production by complex I in nanomolar concentrations. Attempts to elucidate its structure by NMR spectroscopy have failed. Here, by using X-ray crystallographic analysis, we report the structure of NADH-OH bound in the active site of a soluble fragment of complex I at 2.0 Å resolution. We have identified key amino acid residues that are specific and essential for binding NADH-OH. Furthermore, the structure sheds light on the specificity of NADH-OH towards the unique Rossmann-fold of complex I and indicates a regulatory role in mitochondrial ROS generation. In addition, NADH-OH acts as a lead-structure for the synthesis of a novel class of ROS suppressors.
Organizational Affiliation:
Institute of Biochemistry, University of Freiburg, 79104, Freiburg, Germany.