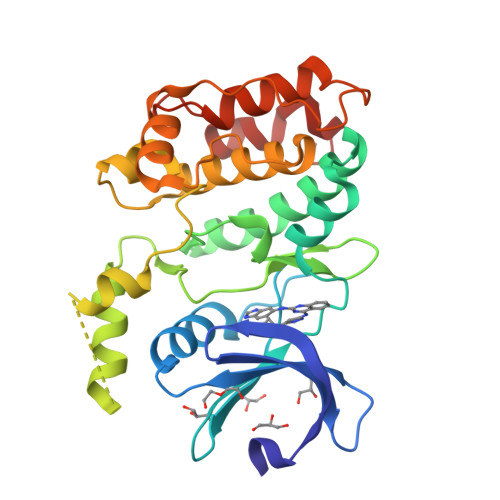
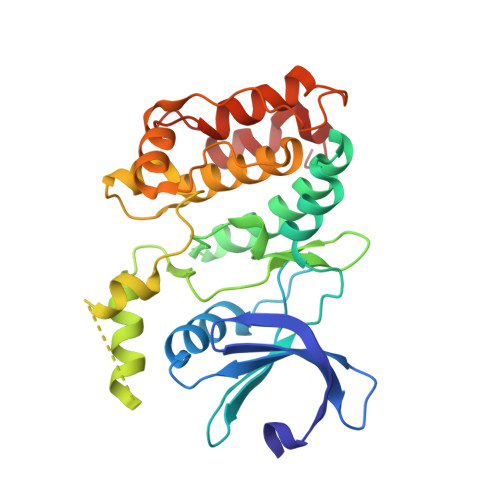
High-Resolution Structure and Inhibition of the Schizophrenia-Linked Pseudokinase ULK4.
Khamrui, S., Ung, P.M.U., Secor, C., Schlessinger, A., Lazarus, M.B.(2020) J Am Chem Soc 142: 33-37
- PubMed: 31841327
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/jacs.9b10458
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
6U5L - PubMed Abstract:
The ULK (UNC51-like) enzymes are a family of mammalian kinases that have critical roles in autophagy and development. While ULK1, ULK2, and ULK3 have been characterized, very little is known about ULK4. However, recently, deletions in ULK4 have been genetically linked to increased susceptibility to developing schizophrenia, a devastating neuropsychiatric disease with high heritability but few genes identified. Interestingly, ULK4 is a pseudokinase with some unusual mutations in the kinase catalytic motifs. Here, we report the first structure of the human ULK4 kinase at high resolution and show that although ULK4 has no apparent phosphotransfer activity, it can strongly bind ATP. We find an unusual mechanism for binding ATP in a Mg 2+ -independent manner, including a rare hydrophobic bridge in the active site. In addition, we develop two assays for ATP binding to ULK4, perform a virtual and experimental screen to identify small-molecule binders of ULK4, and identify several novel scaffolds that bind ULK4 and can lead the way to more selective small molecules that may help shed light on the function of this enigmatic protein.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Pharmacological Sciences , Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai , New York , New York 10029 , United States.