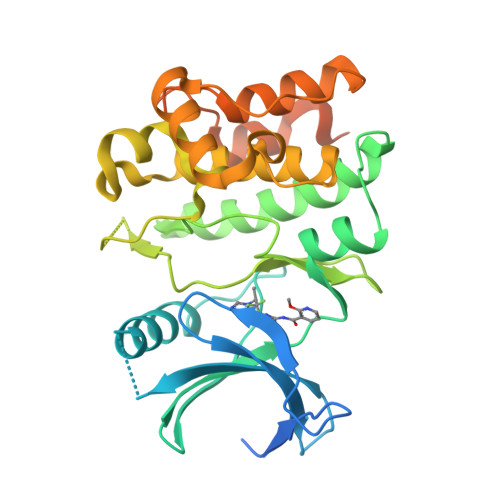
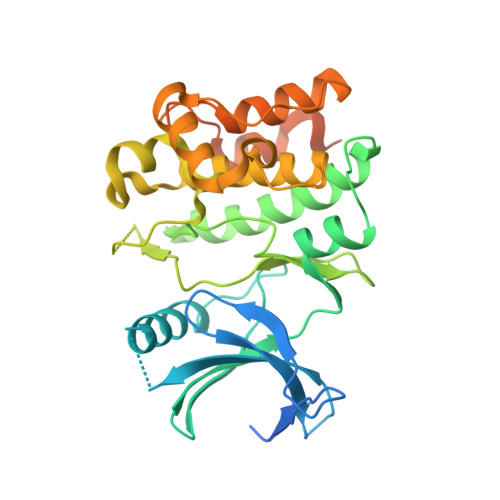
Discovery of Potent, Selective, and Brain-Penetrant Apoptosis Signal-Regulating Kinase 1 (ASK1) Inhibitors that Modulate Brain Inflammation In Vivo.
Jones, J.H., Xin, Z., Himmelbauer, M., Dechantsreiter, M., Enyedy, I., Hedde, J., Fang, T., Coomaraswamy, J., King, K.W., Murugan, P., Santoro, J.C., Hesson, T., Walther, D.M., Wei, R., Zheng, F., Marcotte, D.J., Spilker, K., Kumar, P.R., Liu, Y., Gilfillan, R., Gonzalez-Lopez de Turiso, F.(2021) J Med Chem 64: 15402-15419
- PubMed: 34653340
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jmedchem.1c01458
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
7MU6 - PubMed Abstract:
Apoptosis signal-regulating kinase 1 (ASK1) is one of the key mediators of the cellular stress response that regulates inflammation and apoptosis. To probe the therapeutic value of modulating this pathway in preclinical models of neurological disease, we further optimized the profile of our previously reported inhibitor 3 . This effort led to the discovery of 32 , a potent (cell IC 50 = 25 nM) and selective ASK1 inhibitor with suitable pharmacokinetic and brain penetration (rat Cl/Cl u = 1.6/56 L/h/kg and K p,uu = 0.46) for proof-of-pharmacology studies. Specifically, the ability of 32 to inhibit ASK1 in the central nervous system (CNS) was evaluated in a human tau transgenic (Tg4510) mouse model exhibiting elevated brain inflammation. In this study, transgenic animals treated with 32 (at 3, 10, and 30 mg/kg, BID/PO for 4 days) showed a robust reduction of inflammatory markers ( e.g. , IL-1β) in the cortex, thus confirming inhibition of ASK1 in the CNS.
Organizational Affiliation:
Medicinal Chemistry, Biogen, 225 Binney Street, Cambridge, Massachusetts 02142, United States.