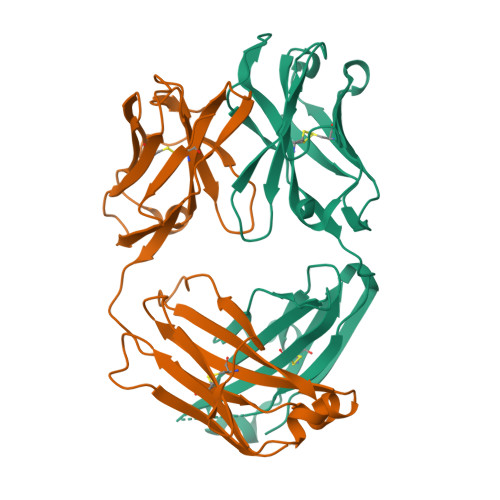
Structural basis for continued antibody evasion by the SARS-CoV-2 receptor binding domain.
Nabel, K.G., Clark, S.A., Shankar, S., Pan, J., Clark, L.E., Yang, P., Coscia, A., McKay, L.G.A., Varnum, H.H., Brusic, V., Tolan, N.V., Zhou, G., Desjardins, M., Turbett, S.E., Kanjilal, S., Sherman, A.C., Dighe, A., LaRocque, R.C., Ryan, E.T., Tylek, C., Cohen-Solal, J.F., Darcy, A.T., Tavella, D., Clabbers, A., Fan, Y., Griffiths, A., Correia, I.R., Seagal, J., Baden, L.R., Charles, R.C., Abraham, J.(2022) Science 375: eabl6251-eabl6251
- PubMed: 34855508
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1126/science.abl6251
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
7SN0, 7SN1, 7SN2, 7SN3 - PubMed Abstract:
Many studies have examined the impact of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) variants on neutralizing antibody activity after they have become dominant strains. Here, we evaluate the consequences of further viral evolution. We demonstrate mechanisms through which the SARS-CoV-2 receptor binding domain (RBD) can tolerate large numbers of simultaneous antibody escape mutations and show that pseudotypes containing up to seven mutations, as opposed to the one to three found in previously studied variants of concern, are more resistant to neutralization by therapeutic antibodies and serum from vaccine recipients. We identify an antibody that binds the RBD core to neutralize pseudotypes for all tested variants but show that the RBD can acquire an N-linked glycan to escape neutralization. Our findings portend continued emergence of escape variants as SARS-CoV-2 adapts to humans.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Microbiology, Blavatnik Institute, Harvard Medical School, Boston, MA 02115, USA.