Amino-acyl tXNA as inhibitors or amino acid donors in peptide synthesis.
Rietmeyer, L., Li De La Sierra-Gallay, I., Schepers, G., Dorchene, D., Iannazzo, L., Patin, D., Touze, T., van Tilbeurgh, H., Herdewijn, P., Etheve-Quelquejeu, M., Fonvielle, M.(2022) Nucleic Acids Res 50: 11415-11425
- PubMed: 36350642
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkac1023
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
7Z5Y, 7Z5Z, 7Z6A, 7Z6K - PubMed Abstract:
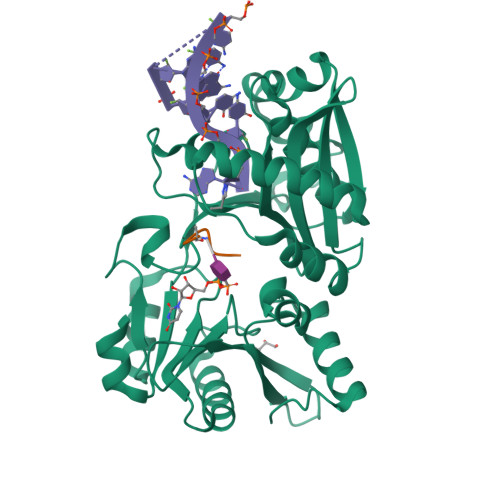
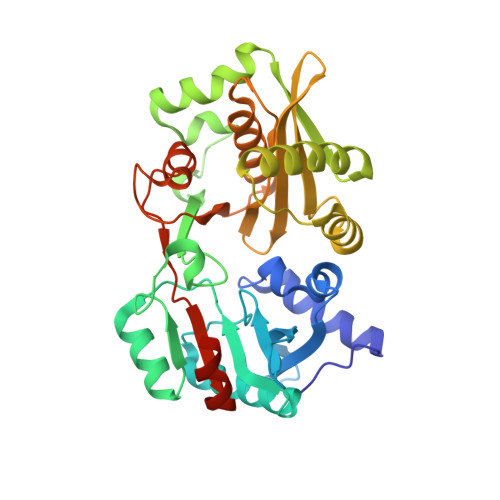
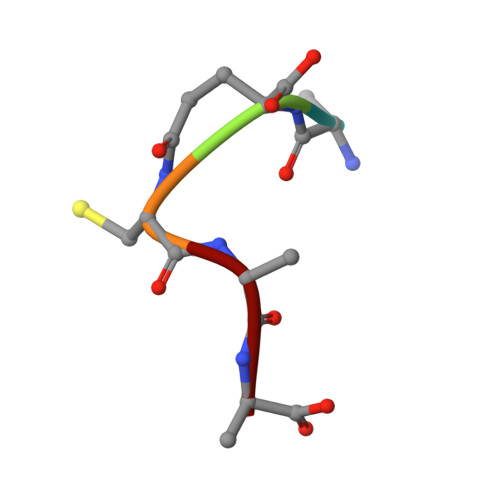
Xenobiotic nucleic acids (XNAs) offer tremendous potential for synthetic biology, biotechnology, and molecular medicine but their ability to mimic nucleic acids still needs to be explored. Here, to study the ability of XNA oligonucleotides to mimic tRNA, we synthesized three L-Ala-tXNAs analogs. These molecules were used in a non-ribosomal peptide synthesis involving a bacterial Fem transferase. We compared the ability of this enzyme to use amino-acyl tXNAs containing 1',5'-anhydrohexitol (HNA), 2'-fluoro ribose (2'F-RNA) and 2'-fluoro arabinose. L-Ala-tXNA containing HNA or 2'F-RNA were substrates of the Fem enzyme. The synthesis of peptidyl-XNA and the resolution of their structures in complex with the enzyme show the impact of the XNA on protein binding. For the first time we describe functional tXNA in an in vitro assay. These results invite to test tXNA also as substitute for tRNA in translation.
Organizational Affiliation:
INSERM UMR-S 1138, Centre de Recherche des Cordeliers, Sorbonne Université, Université Paris Cité, F-75006 Paris, France.